AI, air cargo and email automation: the problem and the opportunity
The volume of email in modern logistics creates a visible bottleneck. First, forwarders and carrier teams receive hundreds of messages each day. Next, staff must extract booking details, check capacity, and confirm rates. As a result, manual processes slow replies and stall cargo communications. The surge in e‑commerce and airfreight demand only increases that pressure. For this reason, operators look to AI to automate repetitive tasks, improve speed, and reduce errors.
AI matters because it reads and acts on unstructured email. For example, systems can convert unstructured email requests into structured records for downstream systems. This converts an informal question into a booking-ready format. IATA notes that these tools can cut average email response times by about 40% and improve customer satisfaction. Also, a 2025 IATA survey showed roughly 65% of major operators using AI-driven email helpers, with adoption rising further in their cargo technology report.
ROI in this space is clear. First, faster email responses increase the chance of a quick booking. Second, fewer errors mean fewer claims and rework. Third, teams handle more queries without hiring. For example, large systems already deal with thousands of inbound messages every day, and some systems process over 10,000 emails daily for big carriers (IATA). Meanwhile, industry analysis shows automation can cut customer‑service costs by up to 30% (GAO), which directly improves margin on low‑value enquiries.
Workflow: email → AI extraction → structured shipment record → booking
Also, teams benefit from a consistent tone and fewer manual lookups. virtualworkforce.ai research shows ops teams move from around 4.5 minutes per email to about 1.5 minutes when the assistant drafts replies and updates systems. Therefore, AI reduces cycle time and reduces workload across shared mailboxes. In short, the problem is email volume; the opportunity is AI-driven automation that returns time to staff and capacity to the business.
CargoAI and the AI assistant: how CargoAI turns messy email into structured shipment data
CargoAI has launched tools that focus on turning messy inbox items into clean booking-ready data. First, CargoAI parses unstructured email and extracts name‑value pairs including origin, destination, weight, dimensions, commodity, and preferred dates. Then, it matches those fields to available capacity and rates. As a result, a forwarder can simply ask for a quote and receive a structured proposal within moments. CargoAI’s offering supports instant quoting, suggested routes, and automated booking steps to speed up the sales funnel.
CargoAI launched an AI assistant that automates parts of the booking flow. The assistant reads the inbound message, extracts shipment details, and either suggests a quote or starts an automated booking. This reduces quote-to-book time and removes the repetitive copy‑paste that slows teams. The product also integrates with airline systems and GHA platforms to check capacity and update records, so confirmations are real‑time.
Workflow: email → AI extraction → structured shipment record → booking
Also, CargoAI’s approach blends large language models with rules and plugins to ensure accuracy. The system extracts shipment attributes and checks data against rate engines, GSAs, and live capacity feeds. In practice, the assistant can parse attachments, propose a cargo booking, and push an automated booking into a carrier or TMS when permitted. The company says its cargocopilot agent tool works across whatsapp and email channels, and that its cargocopilot via api supports third‑party integration. In one pilot, the virtual assistant reduced manual data entry and improved first‑pass accuracy.
Notably, CargoAI launches this capability alongside other market players, and the launch represents a major milestone in our journey to make air cargo operations autonomous. The tool handles routine requests and flags ambiguous ones for human review. For more on automating replies and drafting, see virtualworkforce.ai’s resources on virtual assistant for logistics and AI email drafting for logistics virtual assistant for logistics and AI email drafting.

Drowning in emails?
Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents label and draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.
Automate freight workflows: concrete benefits, KPIs and cost impact
Automation brings measurable gains. First, KPIs such as email response time, quotes per hour, booking lead time, and error rate improve once AI handles routine work. Second, teams can track cost per enquiry and cost per booking to measure business impact. Industry figures indicate that automated support can cut operational costs by up to 30% (GAO). Also, IATA reports up to a 40% faster response time for email handling when AI tools are used (IATA).
Concrete before/after metrics help sales and operations teams. For example, a small forwarder might see quotes per hour double after automation. Meanwhile, agent productivity gains in AI-assisted support studies showed mid‑teens percent improvements in handling complex cases (Generative AI at Work). Those productivity gains translate to more handled enquiries and fewer missed opportunities.
Workflow: email → AI extraction → validation → automated booking or handover
Also, automated booking reduces repetitive approvals for routine cargo shipments. Systems map fields to booking screens, check rules, and either auto‑book or generate a pre-filled booking for quick approval. This approach lowers booking lead time and improves SLA compliance. Moreover, data captured by the assistant feeds analytics—so teams learn where rates slip, which lanes have capacity constraints, and which customers submit ambiguous requests. That insight supports commercial decisions and capacity planning.
Finally, tie KPIs to revenue. Faster email responses increase conversion for time‑sensitive cargo. Fewer errors reduce claims and rework costs. The net effect improves margin and supports scale without equivalent headcount growth. To learn how to scale operations without hiring, read our guide on how to scale logistics operations with AI agents how to scale logistics operations.
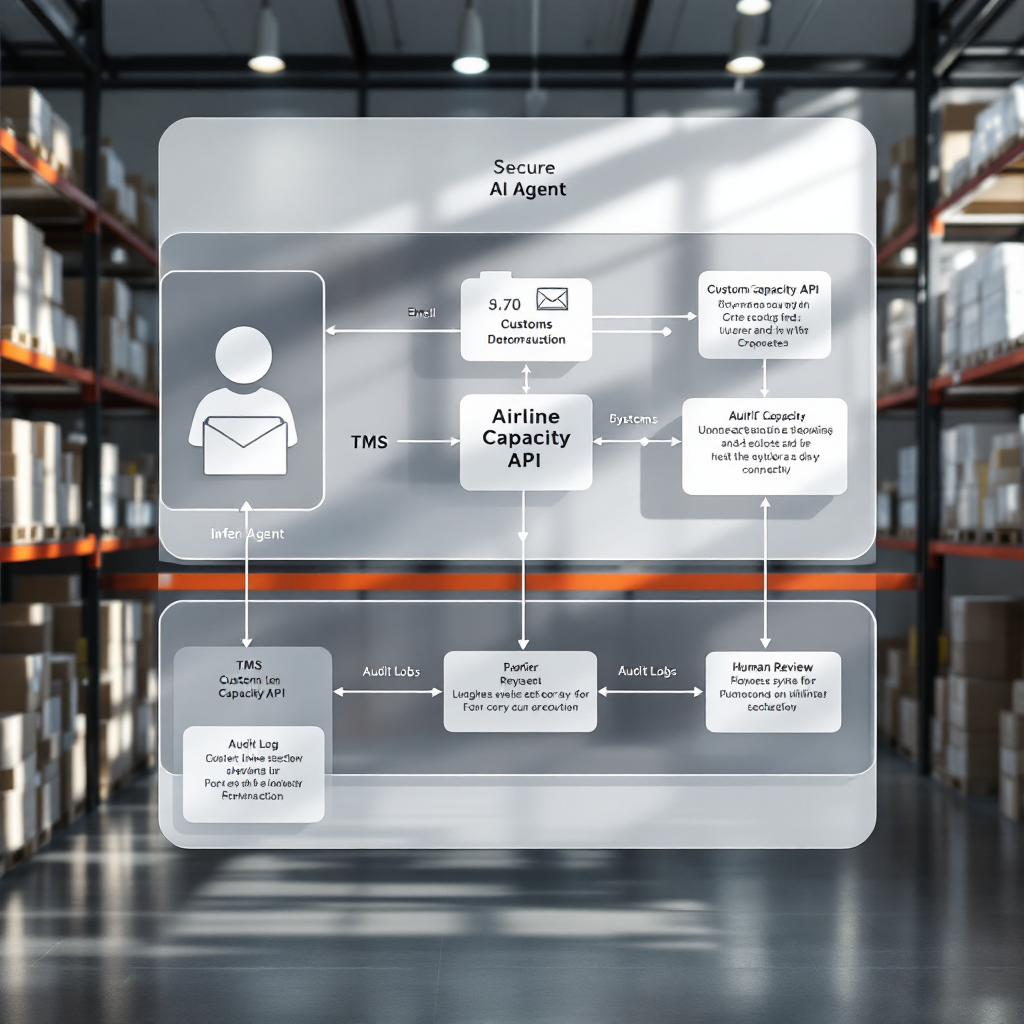
AI agent, logistics integration and compliance: data flows and regulatory needs
Technical and regulatory fit matter. First, an AI agent must integrate with airline capacity sources, TMS/ERP, and customs systems. Second, it must map data to required fields for pre‑arrival screening. For example, ACAS and other customs programs require specific pre‑arrival data; accurate extraction reduces manual errors and delays (ACAS). Therefore, integrations are non‑optional for automated workflows.
Workflow: email → AI extraction → data mapping → customs / carrier / TMS update
Also, the agent needs an audit trail. Every automated action must record the source email, the extracted fields, and the validation result. That record supports compliance and dispute resolution. In practice, the assistant extracts shipment attributes, populates GSAs and AWB fields, and logs changes. The system can perform real-time awb-based tracking and update customers about shipment status. When a match is low confidence, lower-confidence cases are flagged and flagged for human review, which keeps accuracy high while delivering speed without compromising accuracy.
Security and governance are essential. Role‑based access, redaction, and per‑mailbox guardrails prevent leakage. Also, mapping errors commonly occur with dates and commodity codes; the AI must validate against airlines’ rate tables and airline websites. Finally, teams should define escalation rules so edge cases route to specialist staff. For practical steps on email automation with ERP and inbox systems, see our ERP email automation guidance ERP email automation.
Drowning in emails?
Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents label and draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.
Email automation in practice: case studies, operational playbook and common pitfalls
Case studies show clear wins. One forwarder cut manual verification time by more than half after deploying an assistant. Another airline customer reported faster confirmations and fewer misrouted AWBs. Generally, a pilot proves value before full roll‑out. Start with a high‑volume lane, measure KPIs, then expand.
Workflow: pilot lane → scale lanes → full roll‑out with dashboards and SLAs
Common pitfalls include ambiguous emails, poor attachment quality, and inconsistent templates from customers. The AI handles common customer queries to help reduce repeat exchanges, but it can struggle with poorly formatted requests. To mitigate this, implement a human review loop and simple escalation rules. Also, configure templates and training examples that reflect your business rules. This reduces errors and improves first‑pass accuracy.
Operational checklist: route shared inboxes; set SLA rules; define exception paths; retrain staff; install monitoring dashboards. Next, use live reporting to spot lanes with frequent exceptions. That lets you refine AI models and business rules. Studies show AI assistance increases agent productivity, and that customer satisfaction also improves when routine work is automated (QJE).
Also, experiment with channel breadth. The cargocopilot agent can work across whatsapp and email, handling requests such as real-time awb-based tracking and basic rate queries. The assistant to handle common customer issues and the assistant to handle common customer queries both reduce manual replies. When low-confidence answers occur, the system flags them for human review. In short, plan for exceptions, measure rigorously, and iterate quickly. For more on automated logistics correspondence and tools, see our automated logistics correspondence page automated logistics correspondence.
Scale and next steps: adoption roadmap for forwarders and measuring ROI
Adoption follows a clear path. First, pilot a single lane with high volume. Next, integrate the assistant with essential systems and set performance targets. Then expand to more lanes and channels. Finally, measure business outcomes and refine models.
Roadmap steps: pilot (select lanes); integrate APIs; staff training; phased roll-out; continuous improvement.
Key metrics to track include response time, quotes per hour, booking conversion, and cost per enquiry. Baseline these KPIs before the pilot. Use monthly reviews to check progress and adjust rules. Industry figures suggest a payback window often within months, thanks to lower handling time and reduced rework. Remember that automation reduces workload and increases capacity without proportional headcount rises.
Also, align commercial and ops teams so automation supports sales goals. Automated booking and AWB updates should feed CRM and rate engines. For forwarders and airlines, seamless integration improves customer experience and reduces disputes. The journey to make air cargo operations autonomous starts with small wins: faster replies, better data, and fewer manual errors.
Finally, CargoAI and other vendors offer practical tools. For freight forwarders looking for specific solutions, read our guide on AI for freight forwarder communication and the best AI tools for logistics companies AI for freight forwarder communication and best AI tools for logistics companies. Also, watch air cargo news and industry reports for adoption trends—experimenting with AI now gives you a competitive edge.
FAQ
What is an AI assistant for email in air cargo?
An AI assistant reads inbound messages and extracts booking details, rates queries, and tracking requests. It converts unstructured email requests into structured data and can prepare quotes or prefill booking screens for human approval.
How much can AI improve response times?
IATA reports AI email tools can reduce average response time by up to about 40% (IATA). Actual improvement depends on integration depth and the quality of training examples.
Does CargoAI support automated booking?
CargoAI supports workflows that prepare bookings and can push automated booking actions where rules permit. The system extracts shipment fields and can populate carrier booking screens for quick approval.
How do AI agents handle customs pre‑arrival data?
AI extracts required fields and maps them to customs formats, improving compliance with programs like ACAS (ACAS). Low-confidence mappings are routed to human review to avoid errors.
Can the AI work across channels like WhatsApp and email?
Yes. Some agents work across multiple channels. For example, cargocopilot agent tool works across whatsapp and email, handling routine queries and tracking requests.
Will automated replies replace staff?
No. Automation eliminates manual, repetitive tasks and lets staff focus on exceptions and complex customer queries. Human oversight remains critical for low-confidence cases.
How do I measure ROI after deploying an AI assistant?
Measure baseline KPIs such as email response time, quotes per hour, booking lead time, and cost per enquiry. Then track improvements monthly to calculate payback and ongoing value.
Are there security or compliance risks with email automation?
Yes, if not configured correctly. Use role-based access, audit logs, and redaction. Ensure the AI logs changes and references its data sources for compliance and dispute resolution.
What are common pitfalls when deploying email automation?
Pitfalls include poor attachment quality and ambiguous customer emails. Mitigate these by defining escalation rules, templates, and a human review loop for exceptions.
How do I start a pilot with minimal disruption?
Begin with a single, high-volume lane and set clear SLAs. Integrate only essential systems at first, measure results, and scale lanes that show clear ROI. For practical steps, see our guidance on how to scale logistics operations without hiring how to scale logistics operations without hiring.
Drowning in emails?
Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents label and draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.