AI: why managed service providers must adopt AI in managed service delivery
An AI assistant is a software agent that understands context, reads signals, and acts across tools to reduce manual work. For a managed service provider, an AI assistant can triage tickets, draft replies, run diagnostics, and escalate incidents. In short, introducing AI changes managed service delivery by shifting teams from reactive troubleshooting to proactive, predictable operations.
First, adopt speed. AI cuts time on routine work so technicians respond faster. Second, adopt scale. AI lets MSPs handle more clients without hiring at the same rate. Third, adopt security. AI supports threat detection and consistent policy enforcement across client estates. Together, these three business benefits — speed, scale, security — frame why MSPs must add AI to their toolset.
Consider the hard data: “92% of managed service providers are actively integrating AI technologies,” and that single stat explains the momentum behind AI adoption. Further, Microsoft found that “every dollar spent on AI solutions generates an additional $4.90 in the global economy,” which helps justify investment at the board level.
Practically, MSPs use AI for automated ticket triage, proactive monitoring, and threat detection. For example, an AI-powered ticket router can auto-classify incoming messages and route them to the right team. A proactive monitoring model can detect anomalies before they become outages. An AI security layer can spot patterns that indicate an attack and trigger containment steps. These use cases improve response times and increase service quality.
Finally, a short customer stat helps frame impact: many MSPs now report daily AI use that saves human hours and stabilises client SLAs. If you want a deeper example of AI applied to operational email workflows, see how virtualworkforce.ai automates end-to-end email lifecycles, reducing handling time and improving consistency in operational correspondence. For MSPs ready to position your MSP for growth, introducing AI is a strategic move that supports business growth while it enhances operational efficiency.
msp operations: where MSPs gain most from automation
MSP operations show clear hotspots for automation. In practice, the biggest gains come where repetitive tasks dominate time. That includes service desk triage, routine diagnostics, patching, reporting, and on-call escalation. When an MSP applies AI to these areas, teams cut manual triage time and reduce the friction of shared inboxes and incident ownership.
Data shows that many teams already use AI frequently. For instance, “63% of current AI users deploy AI daily,” and those users save roughly 20 hours per month on average. That kind of savings converts directly into more billable work, fewer late-night escalations, and clearer SOPs.
Focus areas and why they matter:
– Service desk triage: AI auto-classifies and prioritises tickets so agents work on higher-value items. This reduces ticket backlog and improves first-contact resolution. – Routine diagnostics and patching: AI-run scripts and playbooks can verify system health and apply patches during maintenance windows. This enhances uptime and cuts repeat tickets. – Reporting and dashboards: AI aggregates metrics to show MTTR, ticket backlog, and trends. These insights improve forecasting and client meetings. – On-call escalation: AI agents surface context and send full audit logs to the next tier, which reduces mean time to repair (MTTR).
Metrics to track include MTTR, ticket backlog, first-contact resolution, and technician idle time. For an operations team looking to streamline, track before-and-after process maps. A simple before/after process map will show long manual flows replaced by a compact AI-enabled workflow. For more on automating email-heavy workflows that many operations teams face, review this practical guide to automate logistics emails with Google Workspace and virtualworkforce.ai automation integration.

To measure ROI for msp operations, calculate time reclaimed per technician, reduction in escalations, and error rate improvements. These metrics link operational change to client satisfaction and retention. Next, pair these KPIs with regular review cycles so the team learns fast and iterates the automation scope.
Drowning in emails? Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.
msps are using ai: common use cases on the service desk and beyond
MSPs are using AI across the service desk and many back-office functions. For day-to-day work, these are the most practical, proven use cases:
– Auto-classify and prioritise tickets so humans focus on complex issues. – Provide resolution playbooks that guide junior technicians. – Client-facing chatbots that handle common questions and escalate when needed. – Asset inventory reconciliation to close gaps between CMDB and reality. – Predictive alerts for device failures or capacity issues, often via predictive maintenance models.
These use cases deliver measurable wins. Daily deployments of AI reduce handling time and free skilled engineers for higher-value problems. However, a warning is worth noting: applying AI to existing processes can yield only micro-productivity gains when new bottlenecks appear. As Bain found, “Applying AI to existing processes often results in only small productivity gains because new bottlenecks emerge” Bain 2025. Therefore, redesign the end-to-end process while you add technology.
How to pilot a single use case in 30 days (quick checklist):
1. Choose one high-volume ticket type and map the current flow. 2. Define success metrics (time saved, FCR, escalation rate). 3. Collect 30–90 days of historical tickets for training and templates. 4. Deploy an AI agent to auto-classify and draft suggested resolutions. 5. Route suggestions to human reviewers and capture feedback for retraining. 6. Measure and iterate every two weeks.
To help MSPS adopt chatbots and ticket automation, virtualworkforce.ai provides end-to-end email automation that ties to ERP, TMS, and WMS data so replies are grounded in facts, not guesses. See our guide on virtual assistant logistics for examples of AI applied to communication-heavy work virtual assistant logistics. For teams that want templates, here is a short ticket prompt you can use: “Summarise the error, list affected systems, propose two remediation steps, and include required escalation.” This template speeds up ticket resolution and improves knowledge management.
ai agent: design, scope and limits of an AI agent for routine automation
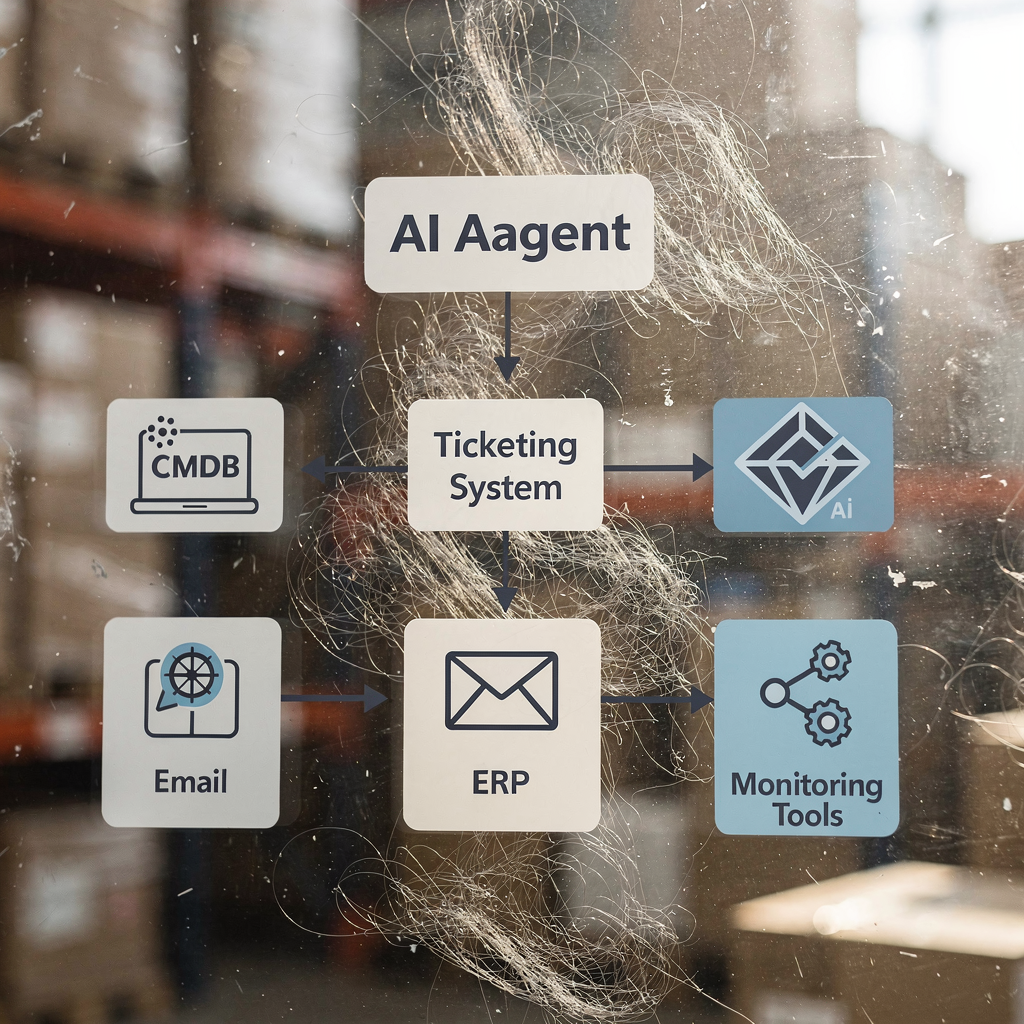
An AI agent is a persistent software actor that runs tasks, preserves context, and escalates when needed. When you implement ai agents, start with clear scope and guardrails. Define the data sources, training signals, escalation paths, and audit requirements before you push the agent into production.
Design points to consider:
– Data sources: logs, ticket history, CMDB, and email threads. The agent must read across systems for accurate context. – Training signals: resolution acceptance, time-to-close, and human feedback. Use these to retrain models. – Guardrails: approve thresholds for automatic action and require human sign-off for high-risk fixes. – Escalation paths: the ai agent should attach full context and recommended steps when it escalates. – Audit logs: record decisions so you can explain actions during reviews and audits.
Limits and risks include a skills gap, legacy tool integration, and regulatory or security checks. The OpenText research highlighted readiness challenges for many organisations, and ISG analysis recommends careful provider selection when implementing AI agents ISG AI Agents Report. You need to account for integration costs and the time to train the agent on domain data.
Minimum data and tooling requirements for a successful ai agent are: ticket corpus, identity and access data, CMDB, logging and monitoring streams, and a secure sandbox for testing. Also include a human-in-the-loop process for the first 60–90 days.
Pilot → measure → scale is the right implementation plan. Pilot a small scope, measure MTTR and error rates, scale to other ticket types, and redesign processes to avoid micro-productivity traps. For email-heavy workflows where context and data grounding matter, consider an ai tool that automates the entire lifecycle of operational email and reduces time per email significantly; learn more about AI for freight forwarder communication as an example of industry application AI for freight forwarders.
Drowning in emails? Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.
business case: ROI, costs and the measurable economics for MSPs who use AI
Building a business case helps get buy-in. Start with a one-page ROI calculator that takes tickets per month, average handle time, technician hourly rate, and expected automation percentage. Use realistic adoption figures: many MSPs report time savings of roughly 20 hours per technician per month when they use AI daily SMB AI Adoption 2025. Translate time saved into labour cost reduction and extra billable capacity.
Include these cost items in your model: licensing, integration, training, change management, and ongoing model maintenance. Also include one-off consulting for data preparation. Don’t forget to model benefits beyond direct labour savings. For instance, Microsoft’s analysis suggests every $1 invested in AI expands economic output by $4.90, which supports wider business growth and client value Microsoft 2025.
Simple ROI example (inputs): tickets per month = 10,000; average handle time = 12 minutes; technician rate = $45/hr; expected automation = 20%. If automation cuts handle time by 50% on automated tickets, you reclaim technician hours that can increase billable work or reduce staffing needs. The board-level summary reads like this: investing in AI assistant capabilities reduces operational costs, improves service quality, and creates capacity to scale service offerings with limited hiring.
Beyond pure ROI, track retention and NPS improvements. AI improves response times and consistency, which drives customer satisfaction. Also account for risk mitigation: AI can improve cybersecurity monitoring and reduce mean time to detect threats. Finally, build scenario models for conservative, likely, and aggressive adoption curves so stakeholders see outcomes under different assumptions. This makes the business case credible and actionable.
ai consulting: closing the skills gap so MSPs can scale AI safely
AI consulting helps close the skills gap that 46% of businesses report as a barrier to successful projects. Your plan should include vendor selection, data preparation, prompt engineering training, governance, and operational roll-out. A good consultant will create a roadmap that trains staff, runs focused pilots, captures SOPs, and expands to other services.
Key offerings to look for from consultants include: vendor-neutral evaluation of ai services, help to implement ai agents, data mapping for CMDB and ticket histories, and training for prompt design and model governance. Consultants should also help with change management, ensuring technicians adopt AI tools and trust suggested actions. For teams that need domain-specific integration—such as logistics or freight communications—look for experience with email automation and grounding in ERP/TMS/WMS data ERP email automation.
Roadmap checklist for ai consulting engagement:
1. Assess current state and pick a starter use case. 2. Prepare data and build a secure sandbox. 3. Run a 30–90 day pilot with human review. 4. Capture SOPs and train staff on the new process. 5. Expand coverage and formalise governance.
This approach reduces failed pilots caused by integration complexity. Also, train for risk management and compliance so you use AI responsibly. Finally, choose partners who deliver end-to-end solutions, not just models, so integration is smooth. For practical resources on scaling without hiring, see how to scale logistics operations without hiring and apply those lessons to managed service teams scale operations guide.
FAQ
What is an AI assistant for MSPs?
An AI assistant is a software agent that automates routine tasks and augments technician work. It can triage tickets, draft replies, run diagnostics, and escalate issues with full context.
How quickly can an MSP pilot an AI use case?
You can pilot a focused use case in 30–90 days if you collect historical tickets and define clear KPIs. Early pilots should include human review to build trust and training data.
What outcomes should I measure first?
Start with MTTR, ticket backlog, first-contact resolution, and time saved per technician. These metrics link automation to cost reduction and better service quality.
Do AI agents replace technicians?
No. AI agents handle repetitive tasks and surface context, which allows technicians to focus on complex issues. This improves job satisfaction and increases capacity.
How do MSPs handle security and compliance when adding AI?
Implement strict guardrails, human-in-the-loop approval for high-risk actions, and audit logs for all decisions. Also involve legal and security teams early in pilots.
What is the typical cost to integrate AI for a small MSP?
Costs vary, but plan for licensing, integration, and training. Use a one-page ROI model to compare expected savings against these costs and justify investment.
Can AI improve cybersecurity for MSP clients?
Yes. AI can enhance threat detection and speed incident response by correlating signals across logs and endpoints. This reduces time to detect and contain threats.
What role does consulting play in scaling AI?
Consultants help with vendor selection, data prep, and governance. They also train staff and build SOPs so MSPs scale AI safely and avoid failed pilots.
How important is data quality for successful AI?
Data quality is critical. High-quality ticket histories, CMDB accuracy, and consistent labels drive model performance and reduce errors in automation.
Where can I see examples of AI applied to operational communication?
Explore case studies of email lifecycle automation that ground replies in ERP and TMS data. For example, virtualworkforce.ai shows how to automate email workflows and reduce handling time while improving consistency.
Ready to revolutionize your workplace?
Achieve more with your existing team with Virtual Workforce.