Why an ai agent matters for courier, logistics and freight
AI is changing how courier firms run day to day work, and an AI agent sits at the center of that change. An AI agent is autonomous software that makes routing, dispatch and customer decisions in real time, and it can act on telematics, booking records, and service rules without constant human input. Large carriers already use these systems. For example, FedEx relies on AI for route optimisation and real-time tracking to cut delivery times and fuel use (source). In boardrooms, the market signal is loud. About 88% of senior executives plan to raise AI budgets in the next year, a sign that AI is moving from pilot projects to core IT investment (PwC). Analysts also expect agentic systems to take on much of routine customer activity; Gartner forecasts rapid growth in agentic AI handling service tasks (Gartner). At the same time, shippers are leaving forwarders that lack modern tools. Research shows that nearly half of shippers say they stopped working with some providers over weak technology (Magaya). That statistic signals real risk for legacy businesses.
Why does this matter to a courier service? First, the AI agent reduces manual routing and decision work, and it helps maintain predictable delivery times and lower fuel spend. Second, it improves customer experience by offering precise status updates and fewer missed runs. Third, it affects margins for freight and parcel work because smarter booking and capacity matching lowers empty miles and underused trucks. An executive quote captures the shift: “AI agents are not just tools; they are becoming autonomous partners that drive efficiency and innovation in courier operations” (source). For managers who want to streamline operations, an AI agent is a strategic tool, not a toy. Finally, remember that good data matters. Poor location or telematics feeds will produce bad decisions, and that problem can create expensive delays and erode customer satisfaction.
If you want to explore how AI fits into email-driven operational workflows, see our page on virtual assistants for logistics which shows how AI can reduce email handling time and improve response accuracy virtual assistant for logistics. Also, teams that automate booking confirmations and tracking messages often start by integrating CRM and TMS data to create a single truth for dispatch and support.
How ai agent can automate dispatch and optimize delivery
Dispatch has long been a manual chore. Now AI can allocate runs in seconds. An AI agent evaluates driver location, SLA, capacity and live traffic, and then it assigns work based on rules and predicted drive time. This reduces manual schedule edits and reduces the hours a dispatcher spends on planning. In practice, agents for delivery use telematics and booking feeds to score tasks. They also reorder stops when a truck has extra capacity or when a time slot becomes more urgent. The result is fewer miles per route and better first-time delivery rates.
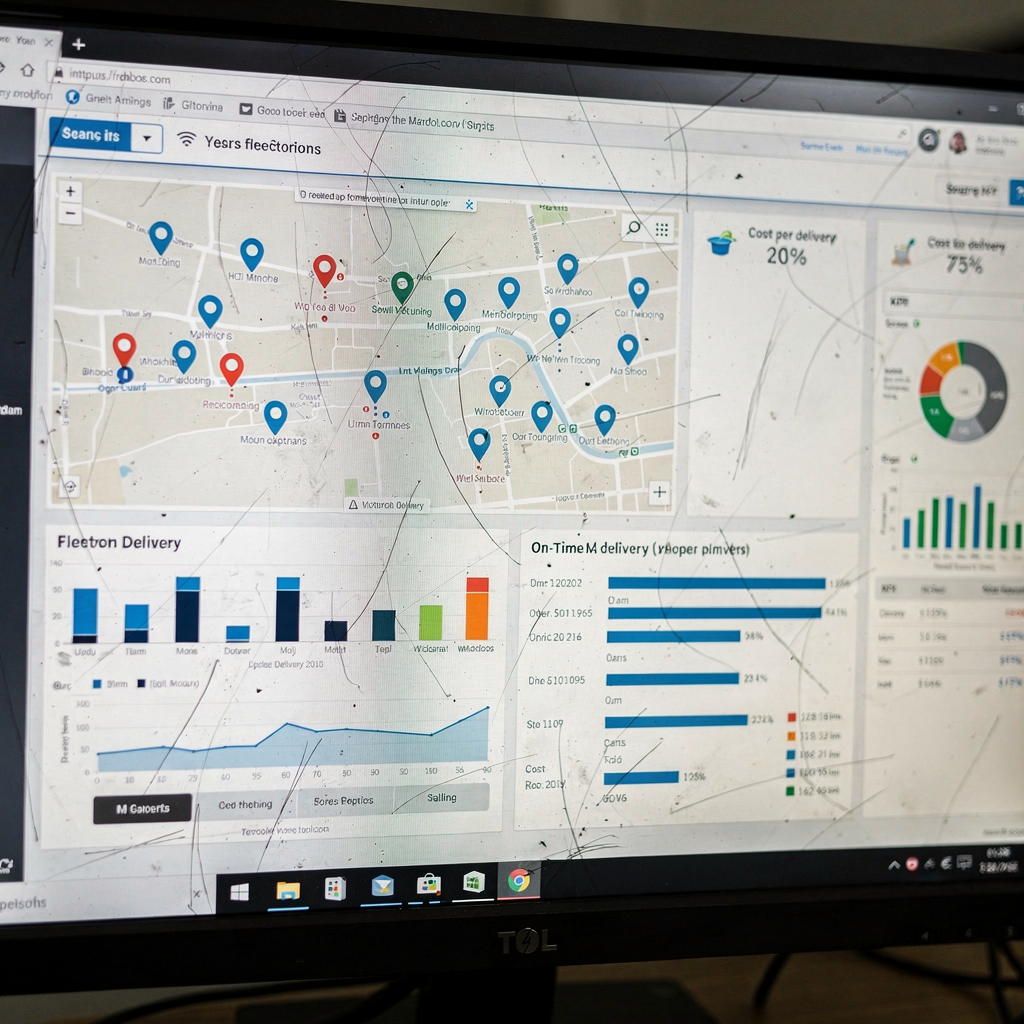
Route optimisation and dynamic re‑routing are vital. The agent pulls live traffic, weather, and priority flags. It then suggests new routes, and it sends real-time tracking to customers. Major carriers show measurable drops in fuel use and faster delivery times when they apply these methods (source). For last-mile work, an AI agent can propose a two‑hour window and tighten that window as the truck moves. That precision reduces missed stops and lowers call volume to customer support. Key KPIs to watch include on-time delivery, first-time delivery rate, cost per delivery, and average route miles. Those numbers show whether the system truly improves operations.
Practical cautions apply. The AI needs high-quality GPS, address, and capacity data. If you collect noisy location data, the agent may send the wrong driver. So invest in telematics and address validation early. Also consider edge processing for low-latency routing decisions and cloud analytics for longer-term learning. Our team often recommends a hybrid model: run routing logic at the edge, and use cloud analytics to improve future routes. When you deploy, start with a constrained region, measure gains, and then scale. For teams interested in reducing repetitive tasks and improving email-driven confirmations, our page on logistics email drafting gives examples of how to automate customer messages and booking confirmations logistics email drafting AI.

Drowning in emails? Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.
Integrate ai agent with crm, omnichannel and conversational query to cut busywork
To get full value from an AI agent you must integrate it with core systems. Connect to TMS, WMS, CRM and telematics so the agent reads a single source of truth. When systems talk, the agent can update records, push status to customers, and generate invoices automatically. That flow reduces email triage and speeds booking confirmations.
Omnichannel tools let customers check status on any channel. Use SMS, app, webchat, WhatsApp, or voice so a consignee can query a status without waiting. A conversational interface is key here. Agents respond to short queries and send real-time updates back to the CRM. This reduces busywork for human teams and raises customer satisfaction. For example, automating routine queries frees agents to handle exceptions and complex claims.
When AI resolves common questions, teams save time. virtualworkforce.ai automates full email lifecycles so operations teams spend less time searching ERP or SharePoint. The platform drafts correct replies, and it can route or resolve messages automatically. That approach cuts handling time and improves consistency. If you want to see practical examples, our automated logistics correspondence case studies show how to connect email, TMS and ERP for automated replies and ticket updates automated logistics correspondence.
Privacy and governance matter. Ask for consent for tracking and notifications. Secure PII and log changes for audits. Use APIs that respect rate limits and error states. Finally, measure effect on ticket volume, average response time, and repeat calls. Those metrics show whether your integrations reduce busywork and increase transparency. Remember to configure escalation paths so only complex issues go to human teams. This keeps agents focused on high-volume, low-complexity tasks and people on exceptions.
How to deploy ai agent at scale for courier service and supply chain automation
Deploying an AI agent across a courier service requires a phased plan. Start with a pilot on a focused route or region. Use canary releases, and validate KPIs before expanding. Track on-time delivery, % automated dispatch, and manual hours saved. These metrics guide rollout decisions and justify further investment. In practice, pilots run 3 to 9 months to show measurable gains. That timeline lets you tune routing logic and update the model with real operational data.
Choose a platform that matches your skills. You can build on open frameworks such as LangChain or Hugging Face if you want to customize models, or buy a vendor product for faster deployment. Either way, connect the agent to TMS, telematics, and ERP via robust APIs. For teams focused on email automation, our guide on scaling logistics operations without hiring explains how to combine AI agents with existing systems for rapid ROI scale logistics operations. Also consider hybrid edge/cloud patterns for latency and resilience. Edge nodes handle time-sensitive routing, and cloud services handle analytics, training, and large-scale model updates.
Security and compliance cannot be afterthoughts. Encrypt PII, protect telematics streams, and retain logs for audits. Define access control and governance, and keep a fallback dispatcher workflow if systems fail. Measure deployment success with practical metrics: reduction in manual dispatch hours, delta in delivery cost per parcel, and % of dispatches automated. When teams see cost and service improvements, they buy in more quickly. Finally, document deployment patterns and create playbooks so operations can configure, customize and maintain the agent without heavy engineering.
Drowning in emails? Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.
How to optimize freight operations and integrate across the supply chain
Optimizing freight requires AI across multiple nodes. AI speeds FTL and LTL quotes and helps match capacity to loads. For moving freight, faster RFQ responses win business. AI systems process pricing models and market data to generate competitive quotes and automate RFQ workflows. They also reduce empty miles by matching available capacity to nearby loads. That lowers cost per shipment and improves asset utilization.
Cross-dock and hub sequencing benefit from agentic decisions. An AI agent can reprioritise loads, reduce dwell time, and sequence pallets to speed throughput. In complex networks, supply chain visibility matters. Combine carrier, forwarder and shipper data to predict delay and trigger corrective action. The academic literature stresses careful data extraction and validation to avoid failed projects; poor extraction and interoperability issues are top causes of failure (source). Use standard APIs and open data formats where possible. That practice reduces integration risk and increases traceability.
When you build a business case, quantify savings. Present cost per parcel saved, CO2 reductions, and lifts in customer NPS. Analysts expect strong market momentum for agentic systems, and executives plan higher AI spend to capture those gains (PwC). Practical tools include freight-matching engines, sequencing optimizers, and real-time tracking dashboards. For those who want examples of AI in freight communications and customs paperwork, our resource on AI for freight forwarder communication shows hands-on automations and email flows AI for freight forwarder communication. Finally, protect against interoperability failures by investing in clean data pipelines and validation routines before full deployment.
faqs: common queries on cost, security, accuracy and next steps
Below are short answers to common questions about adopting AI agents for courier and logistics teams. The section covers ROI timelines, accuracy, job impact, and first steps. If you need deeper help, start with a small pilot and connect CRM, TMS and telematics to measure targeted KPIs.
For a quick guide on integrating email into operational automation, see our page on AI in freight logistics communication which includes practical templates and implementation notes AI in freight logistics communication.
FAQ
What ROI and timeline can we expect from an AI agent pilot?
Pilots typically run between three and nine months to show measurable improvements in KPIs. ROI depends on shipment volume and the current manual baseline, and many teams see handling time and dispatch hours fall significantly once integrations stabilize.
How accurate are delivery predictions and routing decisions?
Accuracy depends heavily on telematics quality, address data, and continuous model training. Monitor predictions, retrain models, and validate against real outcomes to maintain high reliability and reduce missed stops.
Will AI replace dispatchers and frontline staff?
AI reduces repetitive tasks and shifts humans toward exception handling and customer care. Dispatchers still manage complex cases and strategic decisions while AI handles high-volume routine assignments.
How do we secure customer data and comply with regulations?
Encrypt PII in transit and at rest, restrict access by role, and keep audit logs of agent actions. Follow local data rules and obtain consent for tracking and notifications to remain compliant.
What systems must we integrate first for a successful pilot?
Start by integrating TMS, telematics, and CRM so the agent has routing, capacity and customer context. Adding ERP and WMS next expands automation and supports invoice creation and settlement.
How do AI agents handle customer inquiries across channels?
Agents can respond across omnichannel sources such as SMS, webchat, WhatsApp and email, and they can escalate complex cases to humans with full context. This reduces calls and improves customer experience by providing faster status updates.
What is the expected impact on delivery times and customer satisfaction?
Agents often tighten delivery windows and reduce missed runs, which improves customer satisfaction and lowers complaints. Metrics to track include on-time delivery rate and NPS changes after deployment.
How should we measure deployment success?
Track % automated dispatch, reduction in manual dispatch hours, cost per delivery changes, and first-time delivery rate. These KPIs show operational and financial impact and support further deployment decisions.
Can we pilot AI without heavy engineering?
Yes. No-code and low-code vendor solutions let operations teams configure rules and tone, while IT provides secure data access. Start small, validate, and expand to avoid costly rework.
What are good next steps for teams ready to start?
Run a pilot on high-volume routes, integrate CRM, TMS and telematics, and define clear KPIs. For guidance on scaling operations without hiring, consult resources on proven deployment patterns and email automation for logistics operations how to scale logistics operations.
Ready to revolutionize your workplace?
Achieve more with your existing team with Virtual Workforce.