AI assistant: core functions for warehouse management and the supply chain
AI plays a central role in modern warehouse management and supply chain operations. An AI assistant is an AI system that supports picking, packing, inventory and decisions in real time, and it helps teams complete repetitive tasks with higher accuracy. This type of assistant provides voice and visual picking guidance, live task allocation, prioritized order lists, and inventory tracking. It also issues alerts when stock levels shift and can route exceptions to human agents so the team can act fast. For retailers the impact is tangible: retailers report productivity gains of around 20–25% in warehouse operations thanks to optimized task allocation and reduced human error, which NVIDIA documents.
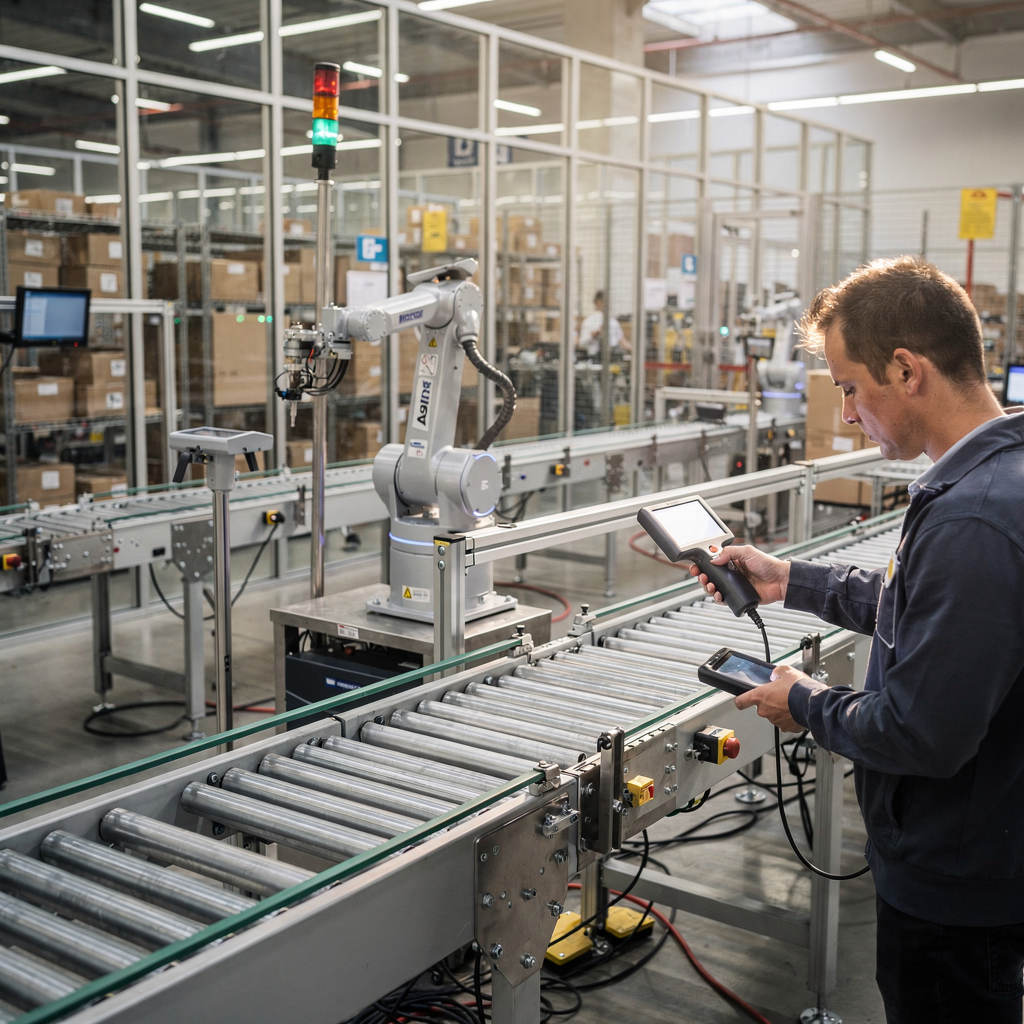
Core tasks covered by AI include inventory tracking tied to a warehouse management system, order prioritisation, pick path routing, and quality checks built into packing stations. For instance, Ocado-style robotics combine automated physical picking with AI planning, and enterprise WMS vendors such as Manhattan Associates or Blue Yonder integrate AI into workflows to prioritize the next best action. These examples show how AI integrates with existing systems to streamline operations and reduce mis-picks. The automated orchestration of tasks helps teams pick more orders per hour and lower fulfillment lead time, and it often improves safety when heavy lifting and repetitive motion are rebalanced between humans and machines.
Why this matters to operations leaders is straightforward. When AI analyzes large amounts of data from POS, ERP, WMS, sensors, and shift rosters, it spots patterns and predicts bottlenecks. This predictive capability reduces manual error and speeds fulfilment, and it helps optimize inventory so fewer stockouts occur. In addition, AI helps to prioritize urgent orders during peak periods. Leaders who want to discover how AI can boost throughput will find quick wins by integrating AI-based routing and tasking into an existing warehouse management system, and by piloting voice or vision-guided picking. Virtualworkforce.ai, for example, focuses on the email-heavy operational workflows that create friction; by automating the lifecycle of operational messages we help DC teams reduce handling time and keep tasking synchronized with ERP and WMS systems, improving response time and traceability.
AI agent and AI tool: demand forecasting, replenishment and optimisation
Different AI approaches exist for demand forecasting and replenishment. An AI agent is an autonomous decision unit that can act without continuous human input, whereas an AI tool is often an analytical or automation module that supports human planners. Both add value, but they play distinct roles: an AI agent can reassign inventory or trigger dynamic replenishment, and an AI tool can produce forecasts, scenarios, and recommended orders for review.
Forecasting accuracy improves considerably when AI models combine internal data with external signals. Studies show AI-driven demand forecasting can improve accuracy by up to 30%, which reduces both stockouts and overstock situations (Silent Infotech). To reach that level, systems ingest POS, ERP transaction feeds, seasonality, promotions, supplier lead times, and external signals such as weather or competitor pricing. A typical modelling pipeline applies feature engineering, time-series models, and machine learning ensembles to produce probabilistic demand that feeds into replenishment engines. This enables dynamic slotting and buffer adjustment, which in turn optimizes shelf and floor stock across the network.
Vendors such as Blue Yonder and other forecasting modules are widely used by major retailers, and they show measurable lifts in inventory turns and forecast accuracy. In practice you should start with a proof of concept: choose a category with stable demand and good historical data, integrate sales and inventory feeds, run the AI models in parallel with existing planning for 30–90 days, and compare outcomes. Use A/B pilots to validate improvements and then scale. When you decide to integrate an AI agent for autonomous replenishment, ensure guardrails are in place so that human planners retain final control over exceptions.
From a data perspective, the inputs required are straightforward but must be clean: POS, ERP, supplier ETAs, promotions calendars, and stock movement logs. The modelling stack can include predictive analytics, gradient-boosted trees, and seasonal decomposition combined with neural forecasting. Machine learning models should be retrained frequently to adapt to new trends and promotions. If you want more details on how to automate shipping and messaging that follows replenishment decisions, see how virtualworkforce.ai automates the email lifecycle so that SAP, TMS, or WMS exceptions are handled automatically and escalated only when needed (virtual assistant for logistics).

Drowning in emails? Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.
AI-powered automation: automate picking, robotics and workflow
AI-powered systems automate physical tasks across the fulfilment lifecycle. Automated Mobile Robots (AMRs), pick-to-light panels, vision systems for SKU recognition, and conveyor control software can operate together to automate picking and packing. These systems use computer vision and AI algorithms to recognize items, validate picks, and guide packers to the right box size. When combined with task batching and route optimisation, they produce measurable throughput gains and fewer mis-picks.
Workflow automation is where software assigns and sequences tasks to maximize efficiency. The system batches orders by zone, balances load across teams, and dynamically reassigns tasks when delays occur. That orchestration relies on real-time telemetry from the floor, and AI decision models that choose the next best action. For example, if a picker is delayed, the orchestration engine can route subsequent tasks to a nearby worker and alert supervisors. This keeps throughput steady and reduces idle time.
In real deployments, robotics firms like Ocado combine custom robots with AI to pick grocery items at high density, and companies use NVIDIA-powered vision to speed product recognition and reduce false rejects (NVIDIA). WMS vendors such as Manhattan embed AI tasking to push optimized pick lists to devices. The expected outcomes include faster throughput, fewer mis-picks, and improved safety as heavy repetitive tasks are automated. These systems also help with compliance; vision checks and automated validations create auditable trails tied back to the warehouse management system and the management system that controls replenishment.
To implement, start by mapping manual tasks and identifying repeatable jobs to automate. Pilot an AMR or pick-to-light in a single zone before expanding. Integrate the automation layer with your warehouse management system and ensure data flows both ways. Use AI algorithms to optimize routing and slotting, and to predict congestion. If emails and exception messages clog operations, consider automation that resolves common queries automatically; virtualworkforce.ai can help automate logistics correspondence so that transport and inventory emails are turned into structured tasks without manual triage (automated logistics correspondence).
Generative AI and AI-driven insights: real-time monitoring and measurable improvements
Generative AI adds a new dimension to operational analytics and reporting. It can draft incident reports, explain anomalies in plain language, and suggest root-cause hypotheses from unstructured logs. For example, a generative AI can read event streams and produce a short incident summary that a manager can act on quickly. This accelerates troubleshooting and frees teams to focus on remediation instead of report writing.
Beyond natural language, AI-driven analytics create dashboards, alerts, anomaly detection, and objective KPIs for picks per hour, OTIF, and inventory accuracy. These dashboards combine structured telemetry with predictive flags that warn of impending stockouts or fulfillment delays. Many organizations now use AI in at least one business function, and retail DCs benefit from consistent, measurable insight into performance; surveys indicate high adoption of these approaches across sectors (Master of Code).
To get measurable outcomes, define baseline metrics then run A/B pilots. Track inventory accuracy, picks per hour, and on-time shipment rates for 30–90 day intervals. Use predictive analytics to forecast the impact of promotions on stock, and then measure actual lift. Industry studies show significant accuracy gains and operational benefits when measurement and retraining are part of the process, and retailers often see reduced shrinkage and better on-time delivery when AI is actively used in operations (Silent Infotech).
Generative AI can also be used to create escalation drafts for customer communication or carrier queries, and to attach the right data from ERP and TMS. If your operations are email-heavy, integrating generative drafts into an automated email workflow reduces handling time and increases consistency. Our company helps teams automate this entire email lifecycle; virtualworkforce.ai routes, resolves, and drafts messages grounded in ERP and WMS so humans intervene only when needed, and responses carry the right context and data (logistics email drafting).
Drowning in emails? Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.
Benefits of AI, customer experience and customer satisfaction
AI delivers operational improvements that directly affect customer experience. Faster fulfilment, fewer stockouts, and more accurate ETAs all translate into higher customer satisfaction. Reduced carrying costs, lower shrinkage, and improved on-time delivery rates also free up margin to invest in better service. Retailers that adopt AI often report better NPS and returning customers as delivery reliability improves.
Linking operation metrics to consumer outcomes is essential. For instance, improved inventory management and better warehouse routing often lead to faster last-mile delivery and fewer returns. Customers receive the right items on time, and they get clearer tracking and estimated arrival times. These changes lift the shopping experience and reduce customer support load. Measures such as fulfillment lead time, return rates, and customer satisfaction score should be tracked alongside internal KPIs to ensure the improvements are visible to the business.
Practically, there are trade-offs. Higher automation density reduces unit cost but can reduce flexibility for unusual orders. Fast throughput can increase packing errors if validation checks are not in place. To balance speed and cost, combine AI-powered validation steps and human oversight where quality matters. Use pilot programs to find the optimal automation density for each location.
Retailers should also track how AI affects customer communication. Automated, accurate updates reduce inbound queries and boost confidence in delivery timelines. If you handle a high volume of operational email, solutions that automate query triage and response can boost response times and reduce manual work. For tailored examples of email automation in logistics and how it lifts customer-facing metrics, see virtualworkforce.ai’s guidance on improving logistics customer service with AI (how to improve logistics customer service with AI).
AI journey and digital transformation for ai in logistics — rollout, risks and measurable ROI
Adopting AI in logistics should follow a phased rollout plan. Start with a pilot in one distribution center and then scale to clusters before adopting network-wide. Focus on quick, measurable wins in the pilot; aim to show improvements in picks per hour, inventory accuracy, and forecast lift within 30–90 days. Define KPIs up front and measure continuously so stakeholders can see the ROI.
Common risks include poor data quality, integration complexity with legacy warehouse management system and ERP, and workforce change management. To mitigate these risks, implement data governance, use middleware to integrate systems, and run change programs for workers. Provide upskilling and clear safety protocols when adding robotics. Ensure data security and access controls as AI models often require sensitive operational feeds.
When choosing vendors, shortlist solutions that integrate seamlessly with existing systems and that offer clear audit trails. Examples of tools include forecasting modules and email automation systems that tie directly into TMS and WMS. Virtualworkforce.ai focuses on the email and exception workload that often blocks scale; our system connects ERP, TMS, WMS and inboxes so transactional queries are resolved automatically and only complex cases are escalated. This reduces handling time and ensures consistent responses without heavy IT work (how to scale logistics operations without hiring).
Finally, the checklist for proof includes KPIs such as productivity percentage gains, forecasting lift percentage, inventory turns, and measurable reductions in handling time or shrinkage. Plan timeline and budgets with staged investments: proof of concept, zone-level automation, and full DC rollouts. Address compliance, safety, and worker engagement early. If you want to learn how AI agents can automate long-running operational workflows such as emails and customs messages, explore our resources on automating customs documentation emails and freight communication to reduce manual triage and speed responses (AI for customs documentation emails).
FAQ
What exactly is an AI assistant in a warehouse?
An AI assistant is an AI-driven system that supports warehouse tasks such as picking, packing, inventory tracking, and real-time decisioning. It provides guidance, automates routine emails and notifications, and helps workers by surfacing the right data from ERP or WMS systems.
How does an AI agent differ from an AI tool?
An AI agent acts autonomously to make decisions or execute tasks with minimal human input, while an AI tool provides analytics or recommendations for humans to act on. Agents can automate responses and routing, whereas tools typically perform forecasting or optimization.
Can AI improve demand forecasting accuracy?
Yes, AI-driven models can improve demand forecasting accuracy by up to 30% when they combine POS, ERP, seasonality and external signals, which reduces stockouts and overstock situations (source). Improvements depend on data quality and model retraining frequency.
Will automation replace warehouse workers?
Automation changes tasks but does not simply replace workers. AI and robotics often remove repetitive physical tasks, and human agents move to supervision, exception handling, and quality assurance roles. Proper training and change management help workers transition.
What metrics should I track to measure ROI?
Track productivity (picks per hour), inventory accuracy, forecast lift, inventory turns, and measurable reductions in handling time for emails and exceptions. Use A/B pilots and 30–90 day ROI checks to validate improvements.
How do I start a pilot for AI in my distribution center?
Start by identifying a high-volume SKU set or a zone with clear manual tasks, integrate sales and inventory feeds, and run AI models in parallel with existing planning for a trial period. Measure outcomes and iterate before scaling cluster-wide.
Are there data security concerns with AI in logistics?
Yes, AI implementations require careful data security and governance since they access ERP, WMS, and customer data. Implement role-based access, encryption, and audit logs to protect sensitive information.
How can generative AI help operations teams?
Generative AI can draft incident reports, explain anomalies in plain language, and propose root causes from unstructured logs. It reduces time spent on reporting and helps teams act faster on exceptions.
What are common pitfalls when adopting AI?
Pitfalls include poor data quality, underestimating integration complexity with a warehouse management system, and neglecting workforce change management. Mitigate these by investing in data governance, middleware, and training.
How does email automation fit into AI for logistics?
Email automation cleans up the largest unstructured workflow in operations by triaging, routing, and drafting replies grounded in ERP and WMS data. Automating email reduces handling time and keeps operational tasks synchronized; our platform virtualworkforce.ai is built specifically to automate the full email lifecycle for ops teams and integrate with existing systems.
Ready to revolutionize your workplace?
Achieve more with your existing team with Virtual Workforce.