ai agent — how agents work and ai agents work in appointment booking
An AI agent is a software entity that performs tasks independently. It can be agentic or task-based. An agentic AI coordinates multiple systems and adapts. A task-based scheduling agent focuses on one flow, for example to book appointments or to confirm time slots. Technically, AI agents work by combining natural language understanding, calendar connectors and lightweight machine learning. They call calendar APIs, apply business rules, and update status in CRM or EHR systems. They also use a knowledge base and simple forecasting models to prioritise slots.
Startups and large firms now integrate AI agents into operational stacks. For instance, 70% of companies now use AI agents as a primary automation lever, and leaders rely on them to reduce manual scheduling time and avoid double-bookings (AI Agent Use Cases to Unlock AI ROI in 2025 (Guide)). C-suite adoption is rising too. Over half of top executives use generative tools regularly, which drives trust in agentic flows (350+ Generative AI Statistics [January 2026]).
Architecturally, the data flow is simple: data sources → agent → calendar/CRM. The agent ingests ERP, booking platforms and email. Then it decides which time slots to hold. It writes back to the calendar. The design needs connectors for calendar APIs, booking platforms and inventory systems. virtualworkforce.ai builds agents that ground replies in ERP and SharePoint so human teams get accurate context; the same pattern applies for appointment booking and for enterprise scheduling (ERP email automation for logistics).
Concrete outcomes are measurable. Teams report fewer double-bookings, faster confirmations and reduced admin hours. A typical scheduling agent can reduce manual scheduling time by two thirds. One practical takeaway: map data sources first. Next, list required integrations. Finally, configure rules for conflict resolution and escalation.
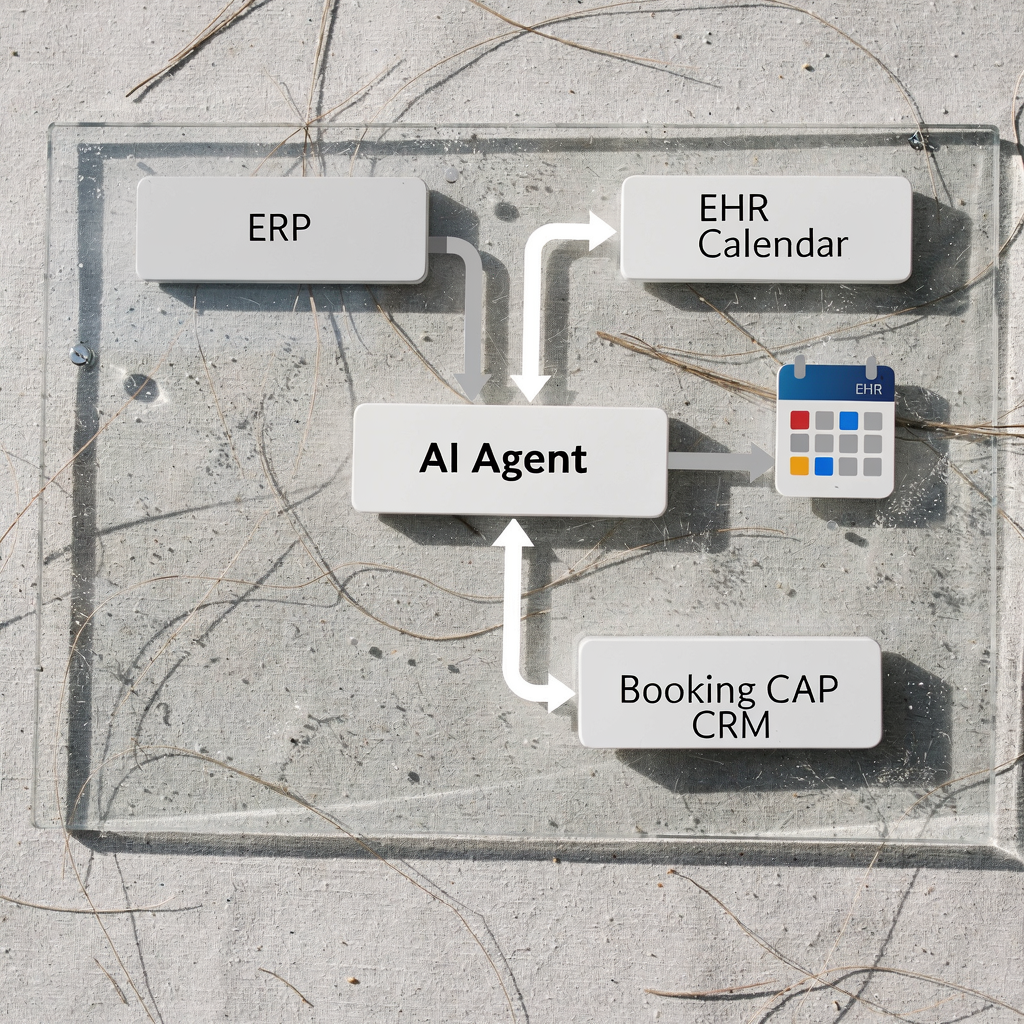
use case: appointment booking and scheduling agent in healthcare and retail
Two strong use cases illustrate the value: healthcare appointment booking and in-store retail demos. In healthcare, a scheduling agent performs triage, confirms clinician availability, syncs with EHR and sends reminders. The agent can reduce missed appointments and free up staff. In retail, an AI-powered booking flow lets customers reserve in-store time for demos, fittings or personal shopping. The bot confirms stock, blocks time slots and triggers staff prep.
For healthcare, track no-show rate, time to confirm and patient throughput. For retail, track conversion uplift, demo attendance and time to confirm. Reports show conversion uplifts between 23% and 35% for AI-assisted booking flows. A realistic case study: a clinic saw 25% fewer missed appointments and 40% less admin time after deploying a scheduling agent that handled reminders and reschedule prompts. When choosing a partner, consider privacy and safety. Health deployments must meet data governance and include fallback to a human operator.
Practical checklist: identify data sources such as EHR, calendar and patient portal. Define privacy rules and SLAs. Include an escalation path to a human customer service agent when clinical judgement is needed. Add an audit trail for each booking. Also, if you need logistics-focused examples of automated correspondence, see how teams automate email workflows at scale (Automated logistics correspondence).
A short example: a retail chain used a simple chatbot to let customers book product demos, which reduced walk-in wait time by 30%. One practical takeaway: design triage rules that prioritise urgent bookings and allow easy reschedule options. That reduces friction and improves customer experience.
Note: when you build a new ai agent for bookings, ensure it respects consent, authenticates users and ties each booking to a reliable source of truth.
Drowning in emails?
Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents label and draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.
booking, real-time and fulfilment: how agents work to check availability
Real-time checks are central to reliable booking. Agents must check inventory, staff rosters, equipment and room schedules. A clear distinction exists between eventual and real-time data. For fulfilment you want real-time status. The agent must reserve resources, block the slot and trigger fulfilment workflows such as prep tasks or order processing. This keeps commitments accurate and customers informed.
Technically, agents use polling or webhooks to maintain sync. Webhooks scale better and cut latency. Use optimistic booking when speed matters, and pessimistic booking where double-bookings risk costs. Add idempotency keys to avoid race conditions. Monitor reconciliation cadence to ensure the agent does not drift from master systems. Measure latency of availability checks and booking success rate.
Inventory checks matter in retail. The agent needs to check inventory and stock availability before confirming an in-store demo. For complex supply chains, integrate inventory systems and ERP data into the data flow. You can also apply demand patterns and light forecast models to hold slots for expected replenishment.
Operational pattern: source availability → try hold → confirm → fulfil. If a hold fails, the agent retries and then alerts staff. For example, in agentic commerce flows McKinsey describes how agents coordinate offers, inventory and fulfilment to deliver a better customer journey (Agentic commerce: How agents are ushering in a new era).
One practical takeaway: log every check with timestamps. Also monitor reconciliation errors daily. That reduces double-bookings and incorrect confirmation messages. Finally, if you want to understand how to scale operations without hiring, read related guidance on workforce automation for logistics (How to scale logistics operations without hiring).
automate workflow and alert: agentic automation to reduce missed appointments
Agents automate the entire scheduling workflow. They handle initial booking, confirmations, reminders, and reschedule flows. They also send cancellation notices and post-visit follow-ups. An agent can free up staff by reducing repetitive work. It can also generate alerts when conflicts appear or when SLA windows slip. Alerts may be email, SMS or a dashboard notification. For teams that manage high email volumes, automating the lifecycle of messages is a proven approach; virtualworkforce.ai focuses on end-to-end email automation to clear inbox bottlenecks (Automate logistics emails with Google Workspace and virtualworkforce.ai).
Decide escalation rules. For instance, if an appointment involves a high-risk clinical decision, the agent escalates to a human. Also set thresholds for high-value clients. Define a human-in-loop window for overrides. Add audit logs to support compliance. Include error handling and retry logic for API failures. This prevents lost bookings and mismatched confirmations.
Operational gains are tangible. Teams report fewer missed appointments, lower staffing costs and fewer manual retries. One realistic metric: a service team reduced missed appointments by 20–30% after adding two reminder messages and one easy reschedule link. Another practical step: give agents a clear rulebook so they escalate correctly. That empowers your agents and keeps quality high.
Checklist item: implement SLAs, set alert channels, and maintain audit trails. Also test alert thresholds in pilot phases to avoid alert fatigue.
Drowning in emails?
Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents label and draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.
conversational ai, customer service ai and prompt design for booking agents
Conversational AI provides the front-end for booking. A chatbot or voice assistant can understand requests and guide customers to book appointments. The interface should use natural language, confirm intent and validate details. For complex queries, the agent can pass context to a customer service agent or a human clinician. Prompt design is crucial. Use short prompts to collect name, date, time slot and contact method. Then confirm choices and ask for consent.
When you design prompts, include graceful fallbacks. For example, if the customer says an unclear date, offer options. Validate identity where required. Use an LLM for contextual replies, but ground responses in a knowledge base to reduce hallucinations. Keep basic chatbot flows for common tasks and escalate otherwise.
Include channels such as WhatsApp and web chat to meet customer preferences. Also make booking flows accessible by voice. Test phrasing to reduce no-shows. For example, a confirmation that states what to bring increases customer satisfaction and attendance. Consider A/B testing reminder timing and phrasing to optimise results.
Prompt example: ask for intent, suggest available time slots, confirm the slot and ask if the customer needs to reschedule later. A practical takeaway: design the conversational flow to minimise steps. That improves conversion. Also track latency targets so responses feel immediate.
faqs and frequently asked questions: risks, integration, ROI of ai agents work
This section answers practical questions about risks, integration and ROI. First, note that AI systems must log decisions and provide audit trails. Second, have a clear policy for human override when agents make risky choices. Third, plan for retries and fallback when APIs fail. Agents don’t replace judgement; they assist staff and automate simple decisions. Teams should also decide who owns the booking record and where the master data resides.
Risk mitigations include retry logic, human review windows and monitoring dashboards. For biased prioritisation, add policy rules and regular audits. For data privacy, follow GDPR or regional rules, and encrypt data in transit. When integrating, map endpoints, configure credentials and test each connector. Consider a phased rollout and a pilot scope that focuses on high-volume, low-risk workflows.
ROI framework: calculate saved admin hours, reduced missed appointments and conversion uplift. Typical payback timelines are 3–9 months for high-volume scheduling tasks. Use a baseline for manual handling time and measure post-deployment metrics. Also forecast staffing impact and redeployment opportunities. If you want to explore options for logistics communication and ROI, see a practical ROI discussion (virtualworkforce.ai ROI for logistics).
Practical next steps checklist: define pilot scope, set success metrics, choose vendor versus custom ai agents, and get stakeholder sign-off. Also ensure the agent can integrate with your CRM and ERP. Finally, keep a knowledge base and update prompts as patterns change.
FAQ
What is an AI agent and how does it differ from a chatbot?
An AI agent is a software entity that can perform tasks autonomously and coordinate systems. A chatbot is often a simpler front-end that handles conversations. Agents handle booking logic, system updates and fulfilment, while basic chatbot flows focus on dialogue.
How do AI agents check availability in real-time?
Agents use webhooks, API calls or polling to query calendars, inventory systems and staff rosters. They then reserve a slot and confirm or retry if the resource is unavailable. This reduces race conditions and double-bookings.
Are AI booking systems GDPR compliant?
They can be when configured correctly. Ensure data minimisation, encryption and clear consent flows. Also keep audit logs and allow customers to request data access or deletion.
Who owns the booking record after an agent confirms an appointment?
Ownership should be defined in your data governance. Typically the CRM or calendar system remains the source of truth. Agents write back to those systems and include references in their audit logs.
What happens when an API call fails during booking?
The agent should implement retry logic, notify staff via alert channels and fall back to human handling if retries exhaust. Logging and SLA rules help teams address persistent failures.
How do I measure ROI for an appointment booking pilot?
Calculate reduced admin hours, improvements in booking conversion and lower missed appointments. Compare staffing costs before and after, and estimate the payback period based on those savings.
Can agents reschedule bookings automatically?
Yes. Agents can offer reschedule options, update calendars and notify affected parties. Always include a human override window for sensitive cases or clinical exceptions.
Do agents handle inventory checks for retail bookings?
They can. Agents query inventory systems to confirm stock availability before committing time slots. This prevents promises that cannot be fulfilled.
Should I build custom AI or buy an off-the-shelf solution?
That depends on scale, complexity and governance needs. Custom AI agents fit specialised workflows but require more engineering. Off-the-shelf solutions speed deployment. Run a pilot to compare outcomes.
How do agents escalate exceptions?
Set rules for escalation to a human customer service agent when conflicts arise, when high-value clients are involved, or when system errors occur. Use email, SMS or dashboards to ensure timely attention.
Drowning in emails?
Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents label and draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.