underwrite faster: how AI-powered genai assistant helps underwriters
First, an AI assistant for underwriting can reduce the steps an underwriter performs on routine risks. For standard submissions the assistant parses forms, extracts fields, validates rules and suggests pricing. As a result, the underwriting cycle shortens. Industry studies report up to a 31% faster underwriting cycle time by linking AI to intake and rule engines. For example, some workflows shrink from three days to three minutes when the assistant handles data intake and template decisions and automates common checks. The assistant acts as an intelligent triage layer that takes on manual tasks and frees underwriters for exceptions. It can read submitted PDFs with AI OCR and normalise values into the policy record. Then, it records results on the policy so an underwriter can review concise rationale. This approach speeds policy issuance and increases throughput, which improves customer satisfaction and retention.
Next, the assistant follows stored underwriting rules and business guideline logic. It uses machine learning for pattern recognition and simple rule engines for compliance. When the assistant can decide, it issues binding quotes and completes policy issuance, reducing rework and cutting turnaround. If a submission falls outside thresholds, the tool escalates to the underwriter with a clear summary and supporting documents. The hybrid flow helps insurance underwriters work faster and reduces human error while maintaining control.
Also, firms can pilot a genai assistant to handle a narrow class of business and then scale. virtualworkforce.ai often maps similar automation patterns from operations to insurance, helping teams automate decisioning and email workflows that support underwriting intake as seen in operational deployments. The result is measurable throughput, lower cycle times and consistent baseline underwriting outcomes.
AI and generative AI in insurance underwriting: performance gains and data sources
Generative AI now complements predictive models to produce clearer underwriting support. For context, some reports show risk assessment accuracy improves by up to 43% when models combine structured and unstructured sources and when carriers integrate broader feeds. C-level executives also back this shift: about 77% of insurance leaders expect generative AI to improve underwriting practices according to an industry survey. These findings explain why insurers build pipelines that connect data sources such as medical records, credit histories, telematics, third‑party feeds and behavioural inputs.
The models on carrier and program level change outcomes. For instance, feature engineering brings in telemetry, prior claims, and policy terms. Models trained on carrier-specific data capture program nuances, so trained models on carrier datasets outperform generic models. When teams combine machine learning algorithms with explainability layers, they can show which features drove a score. This transparency helps underwrite with confidence and helps meet underwriting guidelines and regulator expectations. It also makes it easier to align model outputs with carrier and program rules and program rules to guide users during decisioning.
AI-driven analytics convert unstructured attachments into usable variables. An intelligent underwriting assistant can extract text, normalise values and produce a data set for scoring. The assistant then suggests pricing and flags outliers. Such architecture keeps the underwriting process efficient and auditable. For further ideas on data grounding and enterprise workflows, teams often borrow from logistics automation patterns, such as those described for AI in freight communications to design robust integrations.
Drowning in emails?
Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents label and draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.
automate routine checks and proactive risk assessment to transform the underwriter role
First, automate basic verifications so underwriters can concentrate on complex files. The assistant runs KYC, sanctions, basic health and financial screens automatically. It also performs auto-checks for prior claims and simple exposures. By automating repetitive low-risk checks, the underwriter becomes an exception manager who reviews only non-standard cases. This shift reduces manual process load and improves consistency across the portfolio.
Next, the assistant connects to multiple feeds and assists in proactive risk assessment. It links to third‑party sources and brings comprehensive data to a single view. The assistant connects to structured data and unstructured attachments, and it applies algorithms to analyze patterns across amounts of data. Where items are missing it flags missing items and creates automatic requests for supporting documents. That behaviour supports faster triage and reduces delays. It also creates proactive alerts when emerging signals suggest increased exposure, so underwriting teams can rebalance risk or add conditions.
Then, the solution can present guidance panels during quoting to simplify routine approvals. These panels during quoting and recording present recommended actions and record reviewer choices. The system records the logic, records results on the policy and stores the justification to the results on the policy record. A tool that acts as an intelligent assistant acts as an intelligent flow for quoting and recording results, keeping an auditable trail and reducing human error. For insurers focused on digital intake and correspondence, automated logistics correspondence patterns provide useful parallels for designing escalation and routing rules.
underwriting questions and audit trails: building trust between AI and underwriters
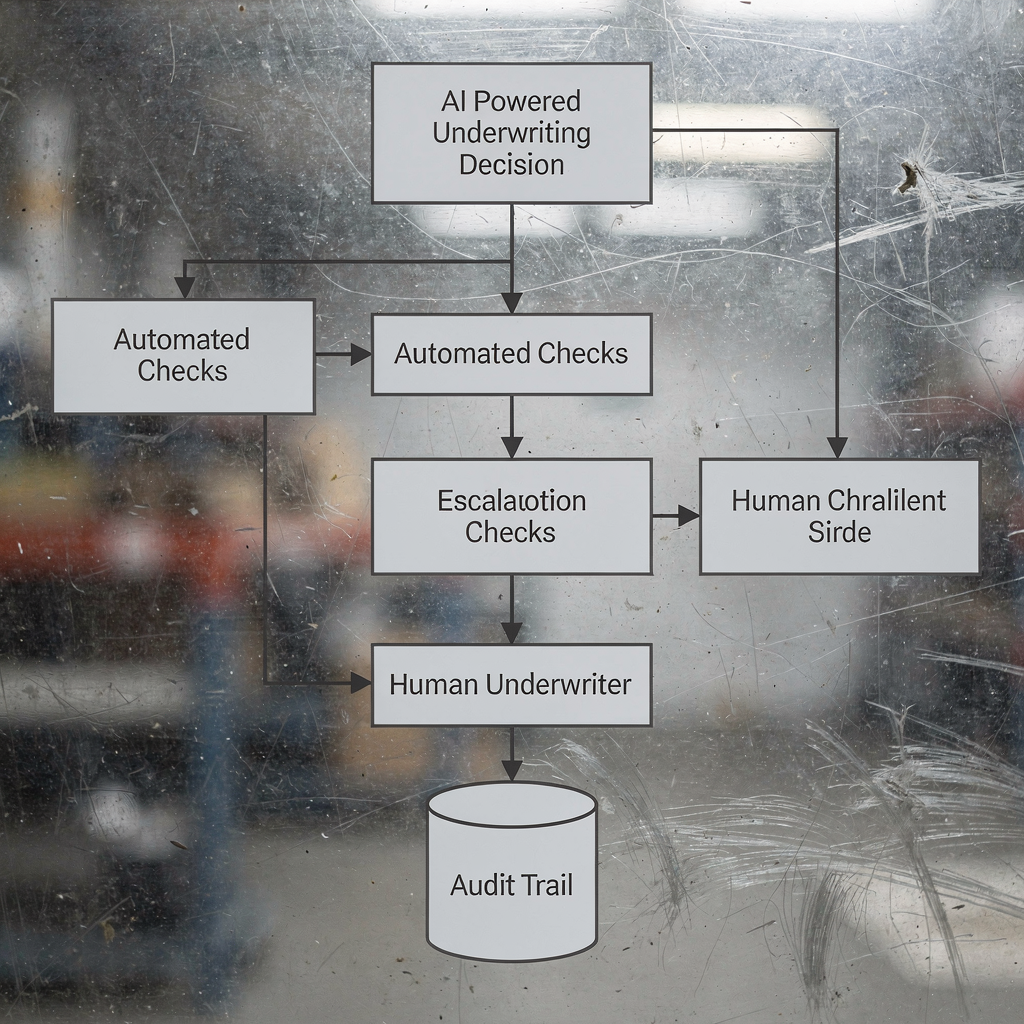
Trust is essential for adoption. Many professionals still prefer human oversight, so the assistant must provide clear audit and explainability features. The system keeps a time-stamped audit log that shows why a decision was made. It attaches score cards, model inputs and a short rationale to each decision, which helps underwriting teams and regulators validate outcomes. The platform also supports stored underwriting records so reviewers can trace earlier rulings and follow precedent.
In practice, the assistant answers underwriting questions from agents and insureds with context. When an agent asks why a rate changed, the assistant retrieves the policy history, the algorithm inputs and the guideline references. This makes responses faster and more consistent. It also reduces back-and-forth emails and supports compliance with underwriting guidelines. Firms can adopt vendor tools like selectsys AI assist alongside internal systems for comparative evaluation and to ensure the audit capabilities meet policy and regulator standards.
Additionally, an audit-ready trail reduces disputes and improves training. Training teams can replay decision flows to identify where models misinterpreted data. This feedback loop supports continuous improvement and helps reduce human error. Overall, a transparent, auditable assistant builds confidence and accelerates AI adoption across the insurer organisation.
Drowning in emails?
Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents label and draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.
ai-powered decision support: flag missing data, reduce errors and accelerate policy issuance
An AI-powered decision layer flags missing information and reduces rework. Inline validation checks fields as documents are uploaded, catching inconsistencies early. The assistant can generate automatic requests for missing data, prioritise outstanding items and score the submission for business impact. By raising clear, actionable tasks the system shortens review cycles and supports faster processing.
Moreover, the assistant helps underwriters make better choices by surfacing ai-driven insights and by quantifying uncertainty. Algorithms to analyze historical claims and exposures enrich the risk score, which enables more accurate pricing and selection. The tool also supports recording results on the policy and wiring those results back into the policy admin system. That direct write path enables near-instant policy issuance for standard risks and reduces queueing for manual review. This reduces manual handoffs and makes the workflow more predictable.
Also, features such as priority scoring and integrated email automation cut turnaround time. Virtualworkforce.ai automates the full email lifecycle in operations; insurers can apply similar flows to policy correspondence to save time and reduce inconsistency by grounding replies in operational data. The combined effect is measurable: fewer errors, lower escalation rates and faster policy issuance, which improves customer experience and operational margins.
Implementing a genai assistant: integration, audit metrics and next underwriting questions
Start with a pilot that defines baseline metrics, such as average cycle time, escalation rate and error rates. Measure before you change processes. Teams should set a phased rollout: pilot, parallel run, scale. Map data sources early, and ensure secure data flows between policy admin, third‑party feeds and email. During pilot, run the assistant in parallel to the existing workflow so underwriters can compare outcomes and provide feedback.
Also, record which trained models on carrier data perform best and when models on carrier and program variants are needed. Establish carrier and program rules to ensure the assistant follows business constraints and create program rules to guide users at the point of decision. You should define KPIs that are measurable and tie back to real-time and historical results. Encourage underwriters to focus on more complex accounts while the assistant handles routine tasks. This balance increases capacity without hiring, a model familiar to financial services teams that adopt automation for volume work.
Finally, maintain governance and a backlog of underwriting questions that the assistant must answer next. Use recorded feedback to refine machine learning algorithms and to grow supporting logic. Include stakeholders from p&c, actuarial and IT, and prepare an audit plan to show regulators the controls. With clear KPIs and staged deployment the rollout will accelerate adoption, simplify operations and deliver measurable ROI. For teams exploring operational AI patterns, see examples of virtual assistant deployments in logistics that demonstrate similar governance and integration needs and transfer those lessons to underwriting.
FAQ
What is an AI assistant for underwriting?
An AI assistant for underwriting is a software agent that supports underwrite tasks by extracting data, applying rules and suggesting actions. It reduces manual tasks and surfaces explanations so underwriters can make informed decisions quickly.
How much can AI speed up underwriting?
Industry studies report cycle time reductions up to 31% in some processes, and some implementations show days-to-minutes improvements for standard risks as organisations automate intake. Results vary by line and implementation depth.
Does AI improve risk assessment accuracy?
Yes. When models combine structured and unstructured data, risk assessment gains can reach as much as 43% in reported cases with the right data pipelines. Explainability and governance are essential to trust those gains.
What routine checks can the assistant automate?
Common examples include KYC, sanctions screening, basic health and financial checks, and document parsing. Automating these checks shortens work queues and lets underwriters focus on exceptions.
How does the assistant handle missing or inconsistent data?
The assistant flags missing data and generates automatic requests for supporting documents, which reduces rework. It can also prioritise items to accelerate issuance for complete, low-risk files.
Will regulators accept AI-made decisions?
Regulators expect audit trails and explainability. The assistant should record rationale, inputs and decision logs to satisfy compliance reviews. That audit capability builds confidence with both supervisors and underwriters.
How do I start a pilot?
Map key data sources, define baseline metrics and run the assistant in parallel. Engage underwriters early, capture their feedback and measure measurable KPIs before scaling.
Can AI handle complex commercial risks?
AI excels at triage and standardised decisions, but complex commercial risks usually require human judgment. The best approach is hybrid: automate routine checks and let humans resolve nuanced underwriting questions.
What data does the assistant need?
Useful inputs include structured policy data, medical records, financial statements, third-party feeds and unstructured attachments. The assistant applies machine learning and rules to combine these sources for better decisions.
How does this compare to other industry uses of AI?
Many industries use AI to streamline unstructured work, such as email automation in operations. Similar principles apply in underwriting, where automation reduces manual processes, improves consistency and frees skilled staff for higher-value tasks. See how operational AI agents automate email lifecycles for parallel insights from logistics deployments.
Drowning in emails?
Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents label and draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.