ai agent and operations teams: what an ai email agent does for ops
An ai agent sits at the centre of email-driven operations. In simple terms, an agent is an ai-powered piece of software that reads, summarises and drafts emails. It can also prioritise threads and flag actions for operations teams. First, it reduces time spent on routine tasks. Then, it frees staff to focus on higher-value strategic work. For example, a shared inbox triage where a virtual assistant scans inbound threads, tags priority messages and assigns ownership shows immediate gains. A small logistics team cut average handling time per mail by several minutes after rollout, and they tracked time saved as a key KPI.
The ai agent performs core tasks. It creates email summarisation for long threads. It generates automated responses for common queries. It updates calendar entries and CRM records with extracted data. In practice, an agent automates repetitive data capture and status updates, so team members avoid copy-paste across ERP and SharePoint. Microsoft reports AI-powered agents can cut time spent on email management by about 40% (Microsoft, 2025), which directly affects response times and workload.
Agents help with context. They create concise summaries, highlight actionable items and surface attachments. Teams spend countless hours hunting for order numbers and proof of delivery. However, an ai email assistant can reduce that friction by citing the right ERP fields inline. For instance, virtualworkforce.ai fuses ERP/TMS/TOS/WMS and email memory to ground replies, which cuts handling time from ~4.5 minutes to ~1.5 minutes per email for many teams. That measured saving becomes part of a broader case for automation and data-driven improvements.
Agents can handle exceptions, too. They flag unusual cases and escalate them for manager review so humans intervene only when needed. In short, agents for operations make communications faster, more consistent and more actionable while lowering the burden of repetitive tasks and improving customer satisfaction.
automate and streamline with an email assistant and shared inboxes
Shared inboxes change how teams coordinate. An email assistant routes messages to the right person, applies templates and prevents duplicated work. For example, when a supplier sends an ETA change, the assistant triages the thread, updates linked CRM records and notifies the duty handler. This single flow reduces handoffs and keeps status updates consistent. Next, the assistant can apply tone and brand voice so replies remain on-message and professional.
Integrations matter here. Agents use connectors to link calendars, crm and third-party automation platforms like zapier. These links let the system create tasks, schedule meeting scheduling slots and push updates to an ERP or a tracking tool. When a shipping delay arrives, the assistant can create a CRM ticket, schedule followup and update a shared tracker. That pattern supports seamless handoffs and fewer missed actions.
One short real-world example is a customer support team using shared inboxes for returns. The email assistant checks warranty status in the CRM, drafts a next-step reply and attaches a return label. The team then measures response SLA and tickets closed per day to track improvement. A key KPI to watch is average response time because faster response times improve customer satisfaction and reduce repeat messages.
When you streamline operations with an email assistant, you also reduce manual effort and errors. Teams avoid needless manual intervention and keep consistent messaging across channels. In addition, using no-code configuration makes deployment fast so business users can change templates and escalation paths without engineering required. If you want a deep example for logistics teams, see our guide on virtual assistants for logistics virtual assistants for logistics.
Drowning in emails? Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents label and draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.
deploy ai without adding headcount to reduce manual effort
Businesses often face rising email volumes and static headcount. Deploy ai to take on routine tasks so teams handle larger volumes without hiring. In sales contexts, UserGems reports tools that consolidate outreach emails and CRM signals can deliver roughly 30% productivity gains (UserGems). Therefore, the business case for automation is strong. For example, a sales ops team used an ai agent to generate quote emails automatically and saw faster deal progression. They tracked closing deals and time to quote as core KPIs.
Headcount planning changes when an agent automates repetitive work. Without adding headcount, operations scale and maintain service quality. Teams see fewer manual steps per ticket and lower hours of manual work per case. For instance, a logistics customer support group that used our tool reduced time per email and measured hours of manual work cut across a week. That metric tied directly to ROI and staffing plans.
Measure success carefully. Use time saved on email and faster quote generation as measurable outcomes. Salesforce notes sales quote automation can reduce quote creation time by 50–70% (Salesforce). Also monitor response SLA, tickets closed and service quality. A standard pilot runs on one mailbox with high volume and low risk. Track error rate and customer satisfaction so you can scale with confidence. If operations teams need examples on how to scale logistics without hiring, consult our guide on scaling operations without hiring how to scale logistics operations without hiring.
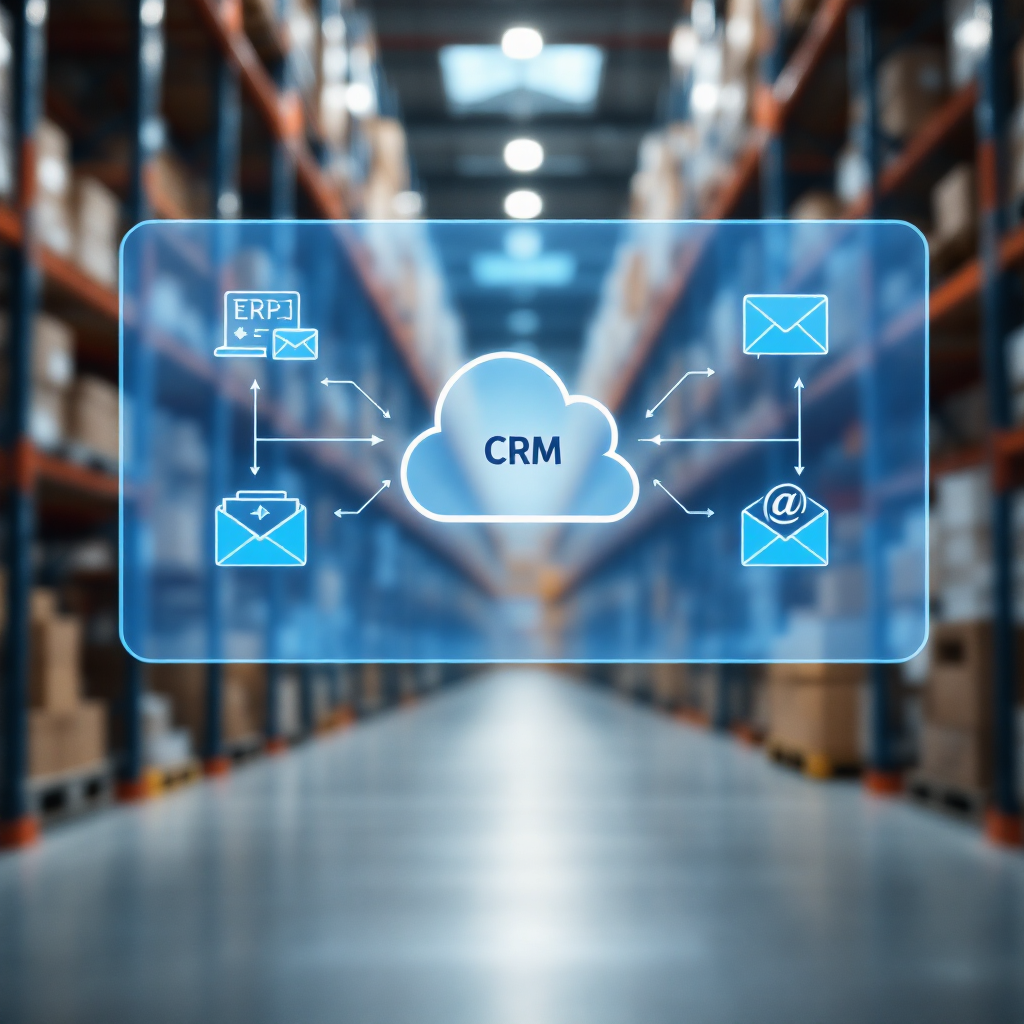
agents operate with CRM, Zapier and custom ai to support scaling and automation
For a systems view, agents operate by reading crm records, triggering zapier flows and calling custom ai models where needed. They can pull order status from an ERP, then create a ticket in the CRM and notify a handler. In this flow, the agent reads crm records and checks business rules before drafting a reply. Next, the system logs the action for audit and analytics so leaders see savings and productivity gains.
Custom ai adds domain knowledge. You can encode tone, escalation rules and SLA expectations. For example, a logistics agent might cite SharePoint packing lists and an ERP status, then send a templated reply that uses the brand voice. That approach ensures consistent messaging across channels. Also, teams can use a no-code interface so business users control templates and handoffs without engineering required.
Scaling requires careful controls. Agents often start small with specific workflows, then broaden scope. You can deploy ai agents that autonomously handle routine tasks and defer complex tasks to humans. For example, when a shipment exception appears, the agent creates a task, drafts a suggested reply and requests manager review before sending. That manager review step reduces risk while enabling rapid scaling without hiring more staff.
If you want a logistics-specific example, see our resource on ERP email automation for logistics ERP email automation for logistics. It explains how to map crm records to email templates and track status updates. By combining a tool that automates repetitive tasks with custom ai and zapier, businesses grow capacity and improve response times while keeping security and audit trails intact.

Drowning in emails? Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents label and draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.
automate workflows and followup to remove manual effort and avoid hiring
Typical flows are predictable. First, the agent triages email. Next, it creates a CRM ticket. Then, it schedules followup and sends a templated reply. These steps let teams automate workflows and eliminate repetitive tasks. For example, a freight-forwarding team used a flow that triaged customs queries, checked customs document status, then returned an update with next steps. That flow cut backlog and improved customer satisfaction.
Followup automation matters. Agents can create automatic reminders, generate followup drafts and apply escalation rules that escalate to a human when thresholds trigger. This reduces missed actions and speeds resolution. A common KPI is response SLA compliance. When followup automates reliably, SLA attainment improves and service quality rises.
Risk controls keep automation safe. Keep a human in the loop for exceptions and complex tasks. For instance, if an agent cannot verify shipment documents in the ERP, it will mark the message for manual intervention. That pattern prevents blind automation and protects data integrity. Also log every decision to maintain audit trails and help with ai adoption and compliance.
Practically, choose inboxes with high volume and low risk for early pilots. Then expand to cover more workflows. Use analytics to monitor tickets closed, hours saved and ROI. virtualworkforce.ai builds ops-tuned agents that ground replies in ERP/TMS/TOS/WMS and SharePoint, reducing manual effort and improving first-pass correctness. By automating followup and using controlled escalation, teams scale without hiring additional staff while keeping quality and control.
frequently asked questions: how to deploy, align with workflow and meet business needs
Start small and measure. First, pick a high-volume inbox with repetitive queries. Then pilot one end-to-end path: email → CRM → task. Measure response times, time saved, error rate and customer satisfaction. Use that data to decide whether to deploy ai agents more broadly. Frequently asked questions about scope, compliance and integration come up during pilots, so prepare clear answers and audit plans.
Map current handoffs before you automate. Identify where manual intervention adds value and where it creates delay. Next, automate one path and keep humans for complex tasks. This approach helps teams adopt automation faster and keeps service quality high. Also ensure IT approves connectors and data access so security and privacy stay intact.
Address business needs and risks early. Define SLA limits, data retention and bias checks. Use loggable decisions and role-based controls so you can review agent behaviour later. If you need practical help, our resources on automated logistics correspondence explain mapping and governance for shipping workflows automated logistics correspondence. For customs-specific flows, see our guide on AI for customs documentation emails AI for customs documentation emails.
Deploy basics include pilot KPIs like time saved on email, tickets closed and SLA attainment. Track hours of manual work removed and compute ROI. Keep a manager review step where needed. Lastly, consider tools that allow no-code configuration so operations teams can adjust templates, escalation paths and brand voice without engineering required. That combination lets teams reduce manual effort and meet business goals while scaling safely.
FAQ
What is an AI email agent and how does it help operations teams?
An AI email agent is software that reads and drafts emails, summarises threads and prioritises messages. It helps operations teams by automating routine tasks, improving response times and reducing manual effort.
How do I start a pilot for an AI agent?
Begin with a high-volume, low-risk inbox and map the current workflow. Then automate one end-to-end path and measure time saved, error rates and SLA performance. Use those metrics to decide the next steps.
What integrations are required for a useful deployment?
Integrations commonly include CRM, ERP, calendar systems and automation platforms like Zapier. Agents that connect to these systems can update crm records and trigger workflows, which reduces manual intervention.
Can I deploy AI agents without adding headcount?
Yes. Deploy ai to take over repetitive tasks so teams scale without adding headcount. Many organisations record measurable productivity gains and lower hours of manual work per ticket.
How do agents handle exceptions and risky cases?
Agents should escalate complex or ambiguous cases for manager review and keep humans in the loop. They also log decisions and provide audit trails to support compliance and troubleshooting.
What KPIs should we track in a pilot?
Track time saved per email, response times, tickets closed and customer satisfaction. Also monitor error rates and ROI to validate business impact.
Are no-code options available for non-technical teams?
Yes. No-code tools let business users configure templates, tone and escalation rules without engineering required. This reduces dependency on IT and accelerates ai adoption.
How do we protect sensitive data when using agents?
Use role-based access, redaction and audit logs. Ensure connectors follow compliance policies and that sensitive fields are excluded or masked in replies.
Do agents improve customer satisfaction?
They can, by providing faster replies and consistent messaging across channels. Measuring response SLA and customer satisfaction helps prove service quality improvements.
Which inboxes should we automate first?
Start with inboxes that handle repetitive queries such as order status, returns or customs documentation. These yield quick savings and clear metrics to expand agents for operations.
Ready to revolutionize your workplace?
Achieve more with your existing team with Virtual Workforce.