Hoe een AI-agent het beheer van de toeleveringsketen in de auto-industrie transformeert
Een AI-agent is een autonome software-entiteit die gegevens waarneemt, beslist en handelt zonder continu menselijk ingrijpen. Eerst neemt hij real-time feeds op van leveranciers, fabrieken en telematica. Vervolgens sluit hij autonome beslissingslussen: detecteren, beslissen en uitvoeren. Dit model verschuift supply chainbeheer van batchprocessen naar continue, geautomatiseerde workflows. McKinsey merkt op dat agentic AI proactieve besluitvorming over de waardeketen mogelijk maakt, niet alleen reactieve automatisering “Agentic AI automatiseert niet alleen taken maar maakt ook proactieve besluitvorming mogelijk”. Ook tonen academische reviews aan dat AI-agenten het beste werken wanneer teams schone data en duidelijke integratiepaden aanleveren Een uitgebreide review van AI-agenten.
In de praktijk bewaakt een AI-agent de voorraad, voorspelt de vraag, plant aanvulling en signaleert uitzonderingen. Bijvoorbeeld gebruiken agenten real-time sensordata van productielijnen en telematica om onderdelen om te leiden en lokale aanvulling te activeren. Ze kunnen takt-tijden optimaliseren en handmatige triage verminderen. In e-mails tussen inkopers en leveranciers kunnen gespecialiseerde AI-agenten intentie extraheren en acties in ERP en TMS pushen. Zie onze gids over geautomatiseerde logistieke correspondentie voor een nadere blik op e-mailgestuurde workflows geautomatiseerde logistieke correspondentie. In proefprojecten rapporteren ondernemingen productiviteitswinsten tot 30–40% in supply chainfuncties en ongeveer 68% van de dealers zag in 2025 positieve AI-effecten in hun ecosystemen adoptiecijfers en marktinzichten.
Om het eenvoudig uit te leggen, verschilt agentic AI van conventionele machine learning-modellen. Machine learning voorspelt patronen. Agentgebaseerde systemen handelen op basis van die voorspellingen en draaien beslissingslussen. Daarom vereist het integreren van een AI-agent datapijplijnen, integratie-API’s en governance. Bedrijven moeten zich richten op datahygiëne, toegangsrechten en consistente berichtformaten. Voor inbound logistiek en operationele e-mail kunnen teams snel resultaat behalen door eerst routinematige verzoeken te automatiseren. Hiervoor demonstreert ons virtualworkforce.ai-product hoe agenten de e-mailafhandelingsduur verminderen terwijl ze ERP en WMS voeden met gestructureerde data ERP-e-mailautomatisering voor logistiek. Tot slot ontdek hoe AI-agenten kunnen werken in de gehele auto-toeleveringsketen door te beginnen met één use case en uit te breiden zodra KPI’s verbeteren.
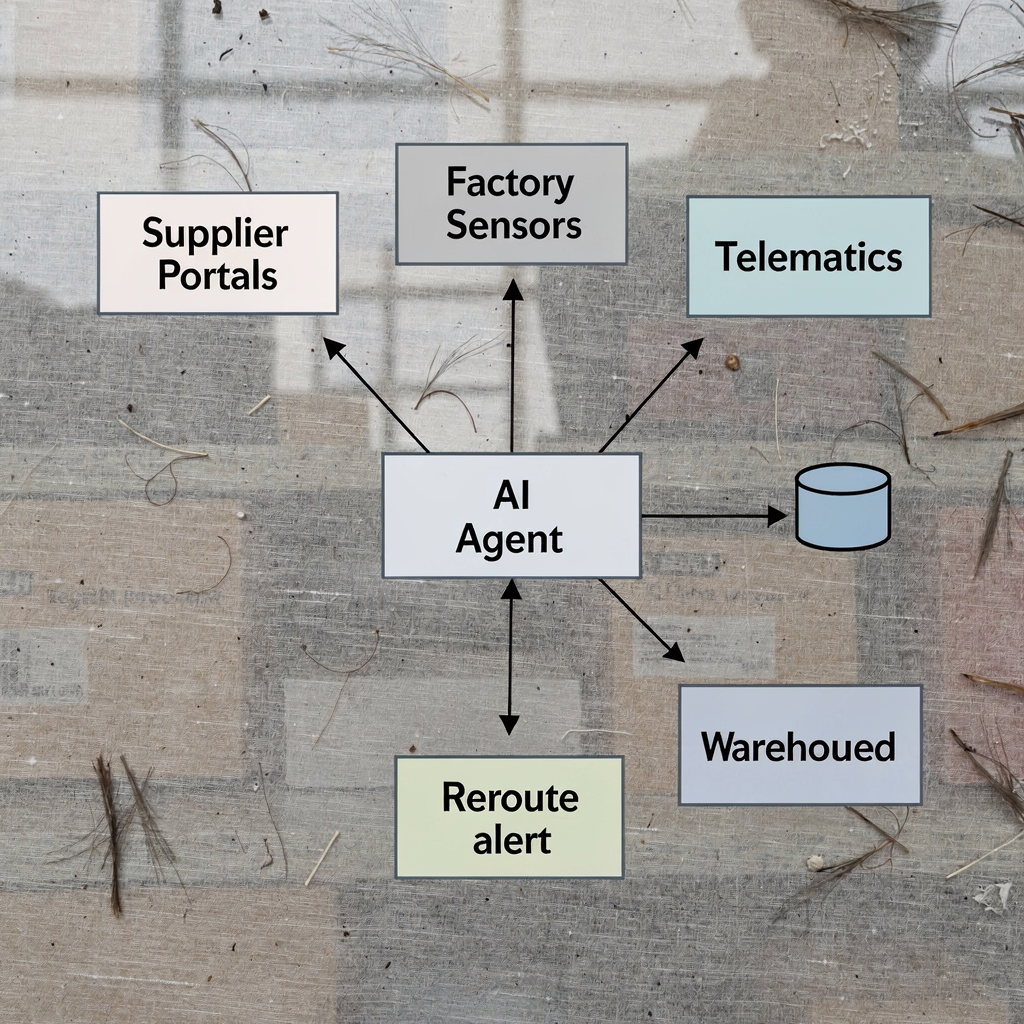
Use cases of AI agents in automotive: demand forecasting, inventory and logistics
Demand forecasting is a primary use case of ai agents. First, agents merge market signals, dealer orders and line output. Then they produce rolling forecasts and safety-stock suggestions. As a result, companies reduce forecast error and lower carrying costs. For example, AI-driven forecasting systems cut forecast error, which reduces stockouts and overstock. Many OEMs and Tier‑1 suppliers now use AI agents in procurement automation and short‑cycle replenishment. These deployments prove that agents provide measurable value in supply chain planning and inventory management.
Second, continuous inventory control is an effective application. Agents monitor multi-warehouse stock in real-time, trigger replenishment orders and rebalance inventory across hubs. They also optimize reorder points and lot sizes. As a consequence, firms shorten lead times and increase inventory turns. In addition, agents feed predictive maintenance schedules into parts planning so service parts reach dealers before failures occur. This integration helps automotive retail and fleet operations.
Third, dynamic logistics and route planning rely on AI to optimize move plans. Agents evaluate carriers, transit time, costs and external events. They can reroute shipments during severe weather or supplier delays, improving on-time delivery. For email-driven logistics coordination, teams can streamline responses with automated drafting and triage; see the logistics email drafting AI resource for examples AI voor het opstellen van logistieke e-mails. Evidence shows better forecast accuracy and faster replenishment cycles after pilots. Moreover, adoption of ai in automotive logistics rose in 2025 and 2026 as companies sought resilience industry analysis.
To quantify, organizations report reductions in carrying costs and up to 30–40% productivity gains in supply chain operations when they combine forecasting, inventory and logistics agents. Therefore, piloting these use cases gives quick ROI. Use a focused pilot, measure forecast improvements and scale with standard APIs and MLOps. This stepwise approach helps automotive companies adopt ai and optimize supply without disrupting core production lines. Finally, discover how ai agents help operations by automating repetitive decision loops and freeing human teams for complex exceptions.
Drowning in emails? Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.
Agentic AI and the role of AI in supplier risk, fleet management and resilience
Agentic AI brings a proactive stance to supplier risk detection and fleet management. First, agents scan supplier performance metrics, contract terms and external signals. Next, they run multi-source risk scoring and flag early warning signs of supply chain disruptions. For instance, an agent can detect component shortages at a supplier, score the risk and trigger an automated contingency playbook that reassigns inventory or reroutes shipments. McKinsey highlights the broad value-creating opportunities of agentic AI across functions inzichten over agentic AI.
Fleet management also benefits. Agents optimize routes, loads, fuel usage and driver schedules using real-time telemetry. They predict delays and propose alternatives. When an agent spots a carrier delay, it can automatically replan loads, notify impacted dealers and adjust arrival promises. These capabilities improve on-time delivery and lower total logistics cost. Agents answer common operational emails and create structured records that feed back into TMS and ERP, reducing manual overhead and improving traceability. For freight-forwarder communication, automated agents have proven effective; companies can see implementation examples here AI voor expediteurcommunicatie.
Implementing agentic systems requires standards for interoperability and supplier data sharing agreements. Real-time telemetry from vehicles and agreed API formats are essential. Also, governance rules must define when agents act autonomously and when they escalate to humans. Organizations must consider change management and the skills gap in AI expertise. Yet agents reduce review cycles and enable faster contingency execution. They also provide clear audit trails for decisions. In short, agents provide improved resilience and measurable benefits when firms align partners, data and governance. Discover how ai agents can detect and respond to disruptions by starting with supplier risk scoring and expanding to cross‑enterprise orchestration.
Leverage AI to optimise logistics, automotive retail and order fulfilment
Use AI to optimise logistics from mode selection to last‑mile delivery. First, agents analyze transport modes, consolidation options and hub locations to reduce cost and transit time. Then they recommend consolidation opportunities and load plans. For automotive retail, agents improve dealer stock allocation and online order promise accuracy. Customers expect accurate delivery promises; Salesforce found 61% of drivers want AI assistance to find and choose cars, which reflects rising expectations for AI in customer experience verwachtingen van consumenten. Therefore, apply agents to order promise, dealer fulfillment and returns handling.
End-to-end logistics optimisation delivers lower transit time and higher on-time rates. For email-heavy logistics interactions, deploying automated reply agents reduces triage time and speeds resolution. Our guide on how to scale logistics operations without hiring gives practical steps for pilots and measurement hoe logistieke operaties zonder personeel op te schalen. Start with a regional pilot. Measure on-time delivery and fill rate. Then expand with standard APIs and MLOps. Also, integrate inbound logistics feeds and customs documentation automation to remove bottlenecks; see an example of AI for customs documentation emails AI voor douane-documentatie-e-mails.
Practical steps include mapping current flows, defining KPIs and establishing escalation rules. Agents should initially handle routine confirmations, routing queries and exception drafts. Next, extend agents to manage consolidation and dynamic reallocation. As a result, dealers receive parts faster and customers see reliable delivery windows. Agents reduce manual work and increase consistency. They also help automotive businesses scale retail operations, improve fill rates and cut logistics cost. Finally, piloting ai with a tight scope yields quick wins and builds confidence for broader rollouts across the automotive sector.
Drowning in emails? Here’s your way out
Save hours every day as AI Agents draft emails directly in Outlook or Gmail, giving your team more time to focus on high-value work.
Benefits of AI agents: measurable ROI, automation advantages and barriers to scale by 2025
AI agents offer clear financial benefits. Companies report lower working capital, fewer stockouts and higher fleet utilisation. Reported productivity improvements range up to 30–40% in supply chain functions, and many dealers reported positive impacts in 2025 productiviteitsgegevens and bevindingen van dealers. Depending on the function, teams can expect 10–30% cost savings through better planning, consolidation and automated email handling. In particular, agents reduce manual email triage and accelerate procurement cycles. Our platform cuts email handling time significantly by automating intent detection and reply drafting, which produces direct labour savings.
Automation benefits go beyond cost. Agents provide faster response to disruption and better decision consistency. They capture institutional knowledge and apply playbooks automatically. Agents reduce cognitive load on planners and dispatchers. They also provide traceability for compliance and audits. However, scaling these benefits requires overcoming barriers.
Main barriers include data quality, legacy IT and partner alignment. Supply chain management isn’t simply a technology upgrade. It needs agreed standards, clean master data and supplier cooperation. Governance and explainability also matter. Teams must define safe operational boundaries where agents act autonomously. Another constraint is the skills gap in ai expertise and change management for shop-floor and procurement teams. Despite these barriers, agentic ai and advanced ai tools make adoption easier when firms pilot, measure and scale. For teams experimenting with ai, start small, define pilots and measure KPIs. Also, ensure you have integration plans and a governance model. The advantages of ai agents are clear, but adoption of ai at scale depends on people, process and technology investments.
Future of AI, future of AI agents and practical roadmap to transform automotive supply chains
The future of ai points to cross‑enterprise orchestration and agent ecosystems. Near term (12–24 months), companies should run targeted pilots in forecasting and logistics while embedding MLOps and secure data pipelines. Next, medium term (2–4 years) will see supplier networks on shared standards and agents coordinating sourcing, production and delivery. Finally, long term (4+ years) promises agentic ecosystems that enable subscription services, personalised delivery and resilient networks. This phased plan helps automotive companies adopt ai and transform processes with measured risk.
Roadmap steps include data readiness, an integration plan, pilot KPIs and governance. In phase one, pick a narrowly scoped use case such as forecast and replenishment or automated replies for freight queries. Then measure forecast error, fill rate and email handling time. For logistics email automation, our resource on automated logistics correspondence shows how to bridge email into ERP and TMS geautomatiseerde logistieke correspondentie. Phase two scales agents across suppliers and carriers. Phase three connects agents into decision fabrics that run continuous optimisation across production and delivery.
Governance must include human-in-the-loop rules, audit logs and compliance checks. Also, invest in ai expertise and change management to drive adoption. Teams should pilot ai in low-risk areas first, then widen scope. Discover how ai can improve resilience by starting with supplier risk scoring and then layering on fleet management. In short, the practical roadmap aligns people, data and tech to transform automotive supply chain planning. By piloting ai, embedding MLOps and scaling through standards, automotive companies will harness the potential of ai agents and see steady ROI over time.
FAQ
What is an AI agent and how does it differ from machine learning?
Een AI-agent is een software-entiteit die input waarneemt, beslissingen neemt en autonoom op die beslissingen handelt. Machine learning levert voorspellende modellen, terwijl agenten handelen op basis van modeluitkomsten en beslissingslussen sluiten.
How can AI agents improve demand forecasting in the automotive industry?
Agenten verwerken dealerbestellingen, sensorfeeds en markttrends om rollende prognoses en veiligheidsvoorraden te genereren. Ze verbeteren de nauwkeurigheid van voorspellingen en verminderen stockouts en overvoorraad.
Are there measurable ROI and productivity gains from deploying AI agents?
Ja. Case studies en markt rapporten tonen productiviteitsverbeteringen tot 30–40% in supply chainfuncties en positieve dealeruitkomsten gemeld in 2025. Deze winst komt door snellere beslissingen en minder handmatig werk.
What are common use cases of AI agents in automotive supply chains?
Veelvoorkomende use cases zijn vraagvoorspelling, continu voorraadbeheer, dynamische routeplanning en predictive maintenance-planning. Agenten verwerken ook operationele e-mails en inkoopworkflows.
How do AI agents help with supplier risk management?
Agenten scoren leveranciersrisico op basis van meerdere bronnen en activeren contingency-playbooks bij verstoringen. Ze detecteren patronen en geven vroegtijdige waarschuwingen zodat teams sneller kunnen ingrijpen.
What governance is required when deploying AI agents?
Governance moet escalatieregels, human-in-the-loop-drempels, auditsporen en data-toegangsbeleid definiëren. Sterke governance zorgt voor uitlegbaarheid en operationele veiligheid.
Can AI agents automate logistics email workflows?
Ja. Agenten kunnen intentie classificeren, antwoorden opstellen en gestructureerde data in ERP, TMS en WMS plaatsen. Zie onze resources over het opstellen van logistieke e-mails met AI voor praktische voorbeelden.
How should companies start piloting AI agents?
Begin met een beperkte use case, definieer pilot-KPI’s, zorg voor schone data en zet integratiepunten op. Meet resultaten en schaal vervolgens met standaard-API’s en MLOps-praktijken.
What barriers slow the adoption of AI agents?
Belangrijke barrières zijn datakwaliteit, legacy-systemen, leveranciersafstemming en het AI-vaardighedentekort. Change management is cruciaal om weerstand te overwinnen en adoptie te waarborgen.
Will AI agents replace human planners in automotive supply chains?
AI zal repetitieve en data-intensieve taken automatiseren, maar mensen blijven essentieel voor strategie, uitzonderingen en relatiebeheer. Agenten vullen mensen aan en maken tijd vrij voor taken met hogere toegevoegde waarde.
Ready to revolutionize your workplace?
Achieve more with your existing team with Virtual Workforce.